Application of array comparative genomic hybridization in Korean children under 6 years old with global developmental delay
- PMID: 29042871
- PMCID: PMC5638834
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2017.60.9.282
Application of array comparative genomic hybridization in Korean children under 6 years old with global developmental delay
Abstract
Purpose: Recent advancements in molecular techniques have greatly contributed to the discovery of genetic causes of unexplained developmental delay. Here, we describe the results of array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and the clinical features of 27 patients with global developmental delay.
Methods: We included 27 children who fulfilled the following criteria: Korean children under 6 years with global developmental delay; children who had at least one or more physical or neurological problem other than global developmental delay; and patients in whom both array CGH and G-banded karyotyping tests were performed.
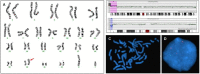
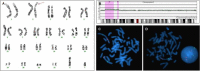
Results: Fifteen male and 12 female patients with a mean age of 29.3±17.6 months were included. The most common physical and neurological abnormalities were facial dysmorphism (n=16), epilepsy (n=7), and hypotonia (n=7). Pathogenic copy number variation results were observed in 4 patients (14.8%): 18.73 Mb dup(2)(p24.2p25.3) and 1.62 Mb del(20p13) (patient 1); 22.31 Mb dup(2) (p22.3p25.1) and 4.01 Mb dup(2)(p21p22.1) (patient 2); 12.08 Mb del(4)(q22.1q24) (patient 3); and 1.19 Mb del(1)(q21.1) (patient 4). One patient (3.7%) displayed a variant of uncertain significance. Four patients (14.8%) displayed discordance between G-banded karyotyping and array CGH results. Among patients with normal array CGH results, 4 (16%) revealed brain anomalies such as schizencephaly and hydranencephaly. One patient was diagnosed with Rett syndrome and one with Möbius syndrome.
Conclusion: As chromosomal microarray can elucidate the cause of previously unexplained developmental delay, it should be considered as a first-tier cytogenetic diagnostic test for children with unexplained developmental delay.
Keywords: Child; Comparative genomic hybridization; Developmental disabilities; Karyotyping.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Array-CGH increased the diagnostic rate of developmental delay or intellectual disability in Taiwan.Pediatr Neonatol. 2019 Aug;60(4):453-460. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Pediatr Neonatol. 2019. PMID: 30581099
-
Array-based comparative genomic hybridization in 190 Korean patients with developmental delay and/or intellectual disability: a single tertiary care university center study.Yonsei Med J. 2013 Nov;54(6):1463-70. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.6.1463. Yonsei Med J. 2013. PMID: 24142652 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical benefit of array-based comparative genomic hybridization for detection of copy number variants in Czech children with intellectual disability and developmental delay.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Jul 23;12(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0559-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31337399 Free PMC article.
-
How to use… microarray comparative genomic hybridisation to investigate developmental disorders.Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2015 Feb;100(1):24-9. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-306022. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2015. PMID: 25189327 Review.
-
Application of array-based comparative genome hybridization in children with developmental delay or mental retardation.Pediatr Neonatol. 2008 Dec;49(6):213-7. doi: 10.1016/S1875-9572(09)60013-9. Pediatr Neonatol. 2008. PMID: 19166117 Review.
Cited by
-
Array-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridization Analysis in Children with Developmental Delay/Intellectual Disability.Balkan J Med Genet. 2022 Jun 5;24(2):15-24. doi: 10.2478/bjmg-2021-0020. eCollection 2021 Nov. Balkan J Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 36249514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeargin-Allsopp M, Murphy CC, Cordero JF, Decouflé P, Hollowell JG. Reported biomedical causes and associated medical conditions for mental retardation among 10-year-old children, metropolitan Atlanta, 1985 to 1987. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1997;39:142–149. - PubMed
-
- Petersen MC, Kube DA, Palmer FB. Classification of developmental delays. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 1998;5:2–14. - PubMed
-
- Shevell M. Global developmental delay and mental retardation or intellectual disability: conceptualization, evaluation, and etiology. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2008;55:1071–1084. - PubMed
-
- Shinawi M, Cheung SW. The array CGH and its clinical applications. Drug Discov Today. 2008;13:760–770. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

