Cardioprotective effect of Notch signaling on the development of myocardial infarction complicated by diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 29042932
- PMCID: PMC5639400
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4932
Cardioprotective effect of Notch signaling on the development of myocardial infarction complicated by diabetes mellitus
Abstract
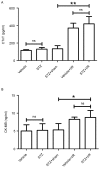
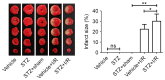
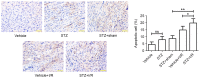
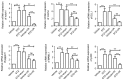
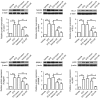
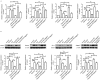
The present study aimed to elucidate the role of Notch signaling in the development of myocardial infarction (MI) concomitant with diabetes in vivo and in vitro and evaluated the therapeutic effect of the Notch signaling in vitro. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats were subjected to 25 min of ischemia and 2 h of reperfusion. Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) isoenzyme levels were detected. Infarct size was measured by 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. Myocardial apoptosis and fibrosis were examined by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling and Masson Trichrome staining, respectively. The mRNA and protein levels of Notch signaling components, including Notch1, Notch4, Delta-like 1, Jagged1, Mastermind-like protein 1 and p300, were quantified by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting analyses, respectively. H9c2 cells were treated with/without 33 mM high glucose (HG) and/or subjected to hypoxia in the presence/absence of Jagged1. Cell viability and apoptosis were determined by MTT assay and Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/propidium iodide assay. Levels of the Notch signaling pathway members were examined. The present findings revealed that diabetes elevated CK-MB and cTnT, increased infarct size, induced myocardial apoptosis and inhibited the Notch signaling pathway in vivo after ischemia/reperfusion. Ischemia/reperfusion augmented the severity of MI in diabetic rats. Furthermore, HG reduced cell viability and induced cell apoptosis in H9c2 cells after hypoxia exposure, which was inhibited by Jagged1. We also found that HG inhibited Notch signaling in H9c2 cells after hypoxia, whereas Jagged1 exerted its cardioprotective effect on hypoxic injury (in HG environments or not) by activating the Notch signaling pathway. In conclusion, these findings suggest that diabetes promoted the progression of MI in vivo and in vitro via the inhibition of the Notch signaling pathway. Jagged1 may protect against MI in in vitro models by activating Notch signaling.
Keywords: Jagged1; Notch signaling; cardioprotection; diabetes mellitus; myocardial infarction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein knockdown alleviates hypoxia-induced myocardial injury in rat cardiomyocytes exposed to high glucose.Exp Ther Med. 2018 May;15(5):4213-4222. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5944. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29725368 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Effect of Echinatin Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Involvement of Hippo/Yes-Associated Protein Signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 11;11:593225. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.593225. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33584269 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective effect of Danshensu against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and inhibits apoptosis of H9c2 cardiomyocytes via Akt and ERK1/2 phosphorylation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan 15;699(1-3):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23200898
-
Research Advances in Myocardial Infarction Repair and Cardiac Regenerative Medicine via the Notch Signaling Pathway.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Mar 19;26(3):26587. doi: 10.31083/RCM26587. eCollection 2025 Mar. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40160574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch Signaling in Ischemic Damage and Fibrosis: Evidence and Clues from the Heart.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Apr 5;8:187. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00187. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28424623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of transcription factor binding motifs promotes Th1 response in Chagas disease cardiomyopathy.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 22;13:958200. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.958200. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36072583 Free PMC article.
-
Notch1 signaling activation alleviates coronary microvascular dysfunction through histone modification of Nrg-1 via the interaction between NICD and GCN5.Apoptosis. 2023 Feb;28(1-2):124-135. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01777-2. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 36241947
-
Hydroxytyrosol protects isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction through activating notch signaling.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(2):217-223. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.81495.17637. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39850112 Free PMC article.
-
ICI-induced cardiovascular toxicity: mechanisms and immune reprogramming therapeutic strategies.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1550400. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550400. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40356915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retracted Article: Knockdown of TUG1 aggravates hypoxia-induced myocardial cell injury via regulation of miR-144-3p/Notch1.RSC Adv. 2019 Jul 25;9(40):22931-22941. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01311c. eCollection 2019 Jul 23. RSC Adv. 2019. Retraction in: RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 26;11(9):5026. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90039k. PMID: 35514492 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
