Intermittent hypoxia simulating obstructive sleep apnea causes pulmonary inflammation and activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
- PMID: 29042934
- PMCID: PMC5639295
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4971
Intermittent hypoxia simulating obstructive sleep apnea causes pulmonary inflammation and activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
Abstract
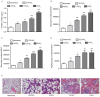
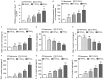
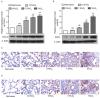
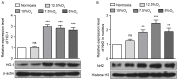
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a disorder with high morbidity in adults. OSA damages multiple organs and tissues, including the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems, the metabolism system, the lungs, liver and heart. OSA-induced damage is earliest and greatest to the pulmonary tissue. The present study established a rat OSA model of differing severity by inducing intermittent hypoxia with different concentrations of O2 and it was determined that OSA caused a severe oxidative stress response and pulmonary inflammation in a dose-dependent manner. OSA increased serum levels of C-reactive protein and 8-isoprostane and elevated the expression of malondialdehyde, tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 in the pulmonary tissue. Furthermore, the expression of two important antioxidants, superoxide dismutase and glutathione, was downregulated following intermittent hypoxia. By contrast, levels of cylooxygenase 2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase, which are crucial in the antioxidative response, increased. In addition, OSA activates the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase (OH)-1 antioxidative signaling pathway. Finally, all increases and decreases in levels of inflammatory and antioxidative substances were dependent on oxygen concentrations. Therefore, the present study demonstrated that OSA, simulated by intermittent hypoxia, caused an oxidative stress response and pulmonary inflammation, and activated the canonical antioxidative Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in a dose-dependent manner. These results may facilitate the development of clinical therapies to treat pulmonary diseases caused by OSA.
Keywords: inflammation; intermittent hypoxia; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; obstructive sleep apnea; oxidative stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpressed long noncoding RNA CPS1-IT alleviates pulmonary arterial hypertension in obstructive sleep apnea by reducing interleukin-1β expression via HIF1 transcriptional activity.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Nov;234(11):19715-19727. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28571. Epub 2019 Apr 14. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30982984
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR-4) Pathway Promotes Pulmonary Inflammation in Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Oct 7;24:7152-7161. doi: 10.12659/MSM.910632. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30293084 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia disturbs insulin secretion and causes pancreatic injury via the MAPK signaling pathway.Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;95(3):415-420. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2016-0167. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28177762
-
Vascular changes, cardiovascular disease and obstructive sleep apnea.Future Cardiol. 2011 Mar;7(2):241-9. doi: 10.2217/fca.10.123. Future Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21453030 Review.
-
Targeting the ROS-HIF-1-endothelin axis as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea-related cardiovascular complications.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Dec;168:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27492897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tempol relieves lung injury in a rat model of chronic intermittent hypoxia via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Dec;21(12):1238-1244. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.31716.7714. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30627367 Free PMC article.
-
Sestrin2 in hypoxia and hypoxia-related diseases.Redox Rep. 2021 Dec;26(1):111-116. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2021.1948774. Redox Rep. 2021. PMID: 34225572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOX4, MDA, IMA and oxidative DNA damage: can these parameters be used to estimate the presence and severity of OSA?Sleep Breath. 2021 Mar;25(1):529-536. doi: 10.1007/s11325-020-02093-2. Epub 2020 May 12. Sleep Breath. 2021. PMID: 32399699
-
Sleep and Oxidative Stress: Current Perspectives on the Role of NRF2.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jun 25;44(1):52. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01487-0. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38916679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Disorders Triggered by Obstructive Sleep Apnea-A Focus on Endothelium and Blood Components.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 12;22(10):5139. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105139. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rozova K, Mankovska I. The effect of intermittent hypoxic training on lung and heart tissues of healthy rats. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2012;80:296–300. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
