The efficacy of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of pediatric arrhythmia and its effects on serum IL-6 and hs-CRP
- PMID: 29042948
- PMCID: PMC5639399
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4960
The efficacy of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of pediatric arrhythmia and its effects on serum IL-6 and hs-CRP
Abstract
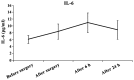
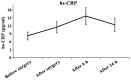
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of pediatric arrhythmia and to assess the changes in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and hs-CRP levels after treatment. Hundred and six children with tachyarrhythmia who were admitted to Xuzhou Children's Hospital from November, 2014 to December, 2015 were recruited for study. The efficacies of radiofrequency in the treatment of different types of arrhythmia were analyzed. Successful ablation was found in 104 cases (98.11%) and recurrence was found in 7 cases (6.73%). Among 62 cases of atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), successful ablation was found in 60 cases (96.77%) and recurrence was found in 3 cases (4.84%). Among 33 cases of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), successful ablation was found in 33 cases (100%) and recurrence was found in 2 cases (6.06%). Among 5 cases of ventricular tachycardia (VT), successful ablation was found in 5 cases (100%) and no recurrence was found. Among 4 cases of atrial tachycardia (AT), successful ablation was found in 4 cases (100%) and recurrence was found in 1 case (25%). Among 2 cases of atrial flutter (AFL), successful ablation was found in both (100%) and recurrence was found in 1 case (50%). After operation, the levels of IL-6 and hs-CRP were increased and were continually increased within 6 h after operation. The levels of IL-6 and hs-CRP at 24 h after operation were reduced but still higher than preoperative levels. The duration of radiofrequency and ablation energy were positively correlated with the levels of IL-6 and hs-CRP, while the number of discharges was not significantly correlated with either. In conclusion, radiofrequency ablation is a safe and effective treatment for pediatric arrhythmia. Postoperative monitoring of IL-6 and hs-CRP levels is conducive to understanding postoperative myocardial injury and inflammatory response.
Keywords: pediatric arrhythmia; radiofrequency ablation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effect of radiofrequency ablation on children with supraventricular tachycardia and the risk factors for postoperative recurrence.Exp Ther Med. 2018 May;15(5):4431-4435. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5986. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29725383 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, Efficacy, and Intermediate-Term Outcomes of Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation for Pediatric Arrhythmias.Cureus. 2020 Sep 16;12(9):e10488. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10488. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33083188 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical characteristics and outcome comparison between atrial fibrillation patients underwent catheter ablation under general aesthesia or local anesthesia and sedation].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 24;45(11):935-939. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2017.11.008. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29166719 Chinese.
-
Role of radiofrequency ablation in the management of supraventricular arrhythmias: experience in 760 consecutive patients.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1993 Aug;4(4):371-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1993.tb01277.x. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1993. PMID: 8269306 Review.
-
[High frequency current catheter ablation in treatment of supraventricular and atrioventricular tachycardia].Z Kardiol. 1995;84 Suppl 2:103-21. Z Kardiol. 1995. PMID: 7571774 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Effect of C reactive protein on the sodium-calcium exchanger 1 in cardiomyocytes.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Aug;22(2):815. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10247. Epub 2021 May 28. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34131438 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
