The long non-coding RNA AK023948 enhances tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 29042961
- PMCID: PMC5639403
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5019
The long non-coding RNA AK023948 enhances tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
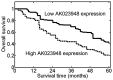
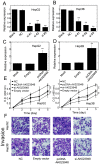
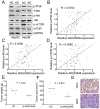
The long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been demonstrated to play pivotal roles in a broad range of processes including tumor biology. However, the exact contributions of lncRNAs to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain poorly defined. In current study, we have unraveled a novel function of AK023948 in HCC. We found that AK023948 was substantially upregulated in tumor tissues. Meanwhile, higher AK023948 expression correlated with poor survival. Upregulation of AK023948 expression can promote HepG2 and Hep3B proliferation and invasion in in vitro experiments. Furthermore, AK023948 also decreased tumor growth in vivo. The tumorigenic role of AK023948 was partially ascribed to PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and AK023948 knockdown decreased pathway activation and tumor growth. These data collectively suggest an oncogenic role for AK023948 and may provide potential insight into therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: AK023948; HCC; PI3K/Akt/mTOR; lncRNA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LncRNA AK023948 is a positive regulator of AKT.Nat Commun. 2017 Feb 8;8:14422. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14422. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28176758 Free PMC article.
-
The long non-coding RNA PTTG3P promotes cell growth and metastasis via up-regulating PTTG1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2018 May 26;17(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0841-x. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29803224 Free PMC article.
-
MYO18B promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Diagn Pathol. 2018 Nov 3;13(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13000-018-0763-3. Diagn Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30390677 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PI3K/AKT is involved in TINAG-mediated promotion of proliferation, invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(1):33-43. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181277. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 29991125
-
Down-regulation of LncRNA NR027113 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Nov;22(21):7222-7232. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201811_16256. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30468465
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through the mTOR Signaling Pathway.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May 25;2021:5596712. doi: 10.1155/2021/5596712. eCollection 2021. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34123955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC00221 silencing prevents the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through let-7a-5p-targeted inhibition of MMP11.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Apr 9;21(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01819-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33836753 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA MAFG-AS1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of miR-6852.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Oct;18(4):2547-2553. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7850. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31572506 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00478-derived novel cytoplasmic lncRNA LacRNA stabilizes PHB2 and suppresses breast cancer metastasis via repressing MYC targets.J Transl Med. 2023 Feb 13;21(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03967-1. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36782197 Free PMC article.
-
The lncRNA ZEB2-AS1 is upregulated in gastric cancer and affects cell proliferation and invasion via miR-143-5p/HIF-1α axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jan 18;12:657-667. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S175521. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30705594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tuo YL, Li XM, Luo J. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 modulates breast cancer cell growth and apoptosis through decreasing tumor suppressive miR-143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19:3403–3411. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
