Warm sparse-dense wave inhibits cartilage degradation in papain-induced osteoarthritis through the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
- PMID: 29042963
- PMCID: PMC5639397
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4984
Warm sparse-dense wave inhibits cartilage degradation in papain-induced osteoarthritis through the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
Abstract
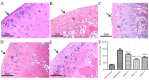
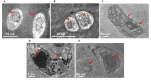
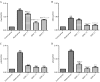
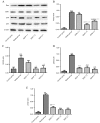
Cartilage degradation is an important in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA). Abnormal activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in chondrocytes promotes an inflammatory response, resulting in the release of chondral matrix-degrading enzymes that accelerate the degradation of cartilage. As a non-pharmaceutical and non-invasive physical therapy regimen, warm sparse-dense wave (WSDW) has been successfully used for the treatment of OA. However, it remains unclear whether WSDW inhibits cartilage degradation in OA through the MAPK signaling pathway. The present study investigated the effects of WSDW on papain-induced OA in rat knee joints. Papain-induced OA was established in rats, which were subsequently divided into a model group and three experimental groups that received a WSDW with the following ratios: WSDW=1:1, WSDW=1:2 and WSDW=2:1. After 12 weeks of treatment, cartilage degradation was evaluated by Mankin scoring of paraffin-embedded sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The changes in cartilage structure were observed by transmission electron microscopy, and the expressions of RAS, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38 and p53 were measured by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis. WSDW was demonstrated to improve the arrangement of collagen fibers, inhibit the tidemark replication and delay cartilage degradation in papain-induced OA. The expressions of RAS, ERK, p38 and p53 in the WSDW (1:2) and (2:1) groups were significantly decreased when compared with the model group (P<0.01). Furthermore, amongst the WSDW groups, the inhibitory effects of the WSDW (1:2) group were typically greater than those of the WSDW (1:1) and (2:1) groups. The results indicate that WSDW may inhibit cartilage degradation in papain-induced OA in rat knee joints by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway.
Keywords: cartilage; osteoarthrosis; signaling pathway; warm sparse-dense wave chondrocyte.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tougu Xiaotong capsule inhibits the tidemark replication and cartilage degradation of papain-induced osteoarthritis by the regulation of chondrocyte autophagy.Int J Mol Med. 2013 Jun;31(6):1349-56. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1341. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23589102
-
Inhibition of p38 pathway leads to OA-like changes in a rat animal model.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012 May;51(5):813-23. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker360. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 22240502
-
Effect of Phellodendron amurense in protecting human osteoarthritic cartilage and chondrocytes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Mar 24;134(2):234-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.12.005. Epub 2010 Dec 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21182922
-
Inhibition of cartilage degradation and suppression of PGE2 and MMPs expression by pomegranate fruit extract in a model of posttraumatic osteoarthritis.Nutrition. 2017 Jan;33:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Nutrition. 2017. PMID: 27908544 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of miR-221-3p contributes to IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation by directly targeting the SDF1/CXCR4 signaling pathway.J Mol Med (Berl). 2017 Jun;95(6):615-627. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1516-6. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28236026
Cited by
-
Senescent skeletal cells cross-talk with synovial cells plays a key role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Feb 28;24(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02747-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35227288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P53: A Key Target in the Development of Osteoarthritis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Jan;66(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00736-9. Epub 2023 May 8. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37154864 Review.
-
Regulation of apoptosis and interaction with cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 27;13:1571448. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1571448. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40213395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Pharmacology and In Vitro Study to Identify the Role of the Active Compounds of Achyranthes bidentata in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Sep 14;26:e925545. doi: 10.12659/MSM.925545. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32925869 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Therapeutic Mechanism of Radix Angelicae Biseratae and Dipsaci Radix Herb Pair against Osteoarthritis: Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Apr 14;2023:2140327. doi: 10.1155/2023/2140327. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37089716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hart HF, Collins NJ, Ackland DC, Cowan SM, Hunt MA, Crossley KM. Immediate effects of a brace on gait biomechanics for predominant lateral knee osteoarthritisand valgus malalignment after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44:865–873. doi: 10.1177/0363546515624677. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andjelkov N, Elvenes J, Knutsen G, Johansen O. Beta-endorphin regulation of MAPKs in cultured human articular chondrocytes: MAPK inhibitors prevent the increase of IL-1 beta protein levels during beta-endorphin stimulation. Cell Commun Adhes. 2007;14:1–8. doi: 10.1080/15419060701224708. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
