Anti-obesity effect of robusta fermented with Leuconostoc mesenteroides in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
- PMID: 29042976
- PMCID: PMC5639269
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4990
Anti-obesity effect of robusta fermented with Leuconostoc mesenteroides in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
Abstract
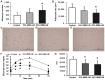
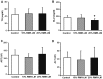
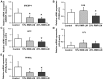
Robusta beans cultivated with Monascus ruber (RMR) were successively fermented with Leuconostoc mesenteroides (LM) and the antiobesity effects were examined. To produce an obese mouse model to investigate the hypolipidemic effects, ICR mice were fed the same high-fat diet for 6 weeks. Treatment groups were given 10 or 20% RMR-LM. Body weight changes in the 20% RMR-LM group were lower compared with those in the control group. Visceral adipose tissue weight and adipose size were significantly lower in the 20% RMR-LM group compared with those in the control group. Significant improvement in glucose tolerance was observed in the 10 and 20% RMR-LM groups compared with the control group. The 20% RMR-LM group exhibited a significant reduction in serum glucose concentration. Hepatic mRNA levels of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1, fas cell surface death receptor, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, which are associated with lipid, and fatty acid metabolism, in the 20% RMR-LM group were significantly lower compared with those in the control group. The results of the present study demonstrated that 20% RMR-LM may be used to prevent obesity, and ameliorate diabetes and lipid metabolism imbalances.
Keywords: Leuconostoc mesenteroides; Monascus ruber; anti-obesity; high-fat diet; robusta.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Red mold rice prevents the development of obesity, dyslipidemia and hyperinsulinemia induced by high-fat diet.Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Nov;32(11):1694-704. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.156. Epub 2008 Sep 16. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. PMID: 18794894
-
Pistachio Consumption Prevents and Improves Lipid Dysmetabolism by Reducing the Lipid Metabolizing Gene Expression in Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Nutrients. 2018 Dec 1;10(12):1857. doi: 10.3390/nu10121857. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30513740 Free PMC article.
-
Eburicoic Acid, a Triterpenoid Compound from Antrodia camphorata, Displays Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects in Palmitate-Treated C2C12 Myotubes and in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 2;18(11):2314. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112314. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29099085 Free PMC article.
-
Monascus pilosus-fermented black soybean inhibits lipid accumulation in adipocytes and in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2015 Apr;8(4):276-82. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60330-8. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2015. PMID: 25975498
-
Antiobesity Effects of Short-Chain Chitosan in Diet-Induced Obese Mice.J Med Food. 2018 Sep;21(9):927-934. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2017.4115. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Med Food. 2018. PMID: 30183503
Cited by
-
Polysaccharide from Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma Attenuates the Progress of Obesity-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Modulating Intestinal Microbiota-Related Gut-Liver Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 13;23(18):10620. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810620. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142520 Free PMC article.
-
Multilocus Sequence Typing of Leuconostoc mesenteroides Strains From the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 25;12:614286. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.614286. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33584616 Free PMC article.
-
Leuconostoc Citreum Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis by Inhibiting p38 MAPK/Erk 44/42 and Stimulating AMPKα Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 17;24(8):7367. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087367. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choudhary M, Grover K. Development of functional food products in relation to obesity. Funct Foods Health Dis. 2012;2:188–197.
-
- Kim H, Jeong JH, Shin JY, Kim DG, Yu KW. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activity of mulberry (Morus alba) leaves fermented with Hericium erinaceum mycelium by solid-state culture. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2011;40:1333–1339. doi: 10.3746/jkfn.2011.40.9.1333. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
