Antiplatelet drug ticagrelor delays gastric ulcer healing in rats
- PMID: 29042978
- PMCID: PMC5639414
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4955
Antiplatelet drug ticagrelor delays gastric ulcer healing in rats
Abstract
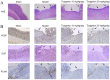
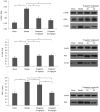
Adenosine diphosphate P2Y12 receptor antagonist clopidogrel is not sufficiently safe for the gastric mucosa in patients with high risk of peptic ulcer, since it may impair healing of gastric erosions. However, the safety of the novel P2Y12 receptor antagonist ticagrelor in the gastric mucosa has not been elucidated to date. The present study aimed to examine whether ticagrelor delays gastric ulcer healing and to elucidate the involved mechanisms. Gastric kissing ulcers were produced in rats by luminal application of acetic acid solution, and ticagrelor was administered at dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg/day orally for 7 days. On day 8 after ulcer induction, the ulcer size, mucosal epithelial cell proliferation of the ulcer margin, expression levels of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and signal transduction pathways for cell proliferation and angiogenesis were measured and compared between the ticagrelor-treated and untreated model groups. The results revealed that the ulcer size was significantly greater in the ticagrelor-treated group compared with the model group, while the mucosal epithelial cell proliferation of the ulcer margin was significantly decreased in the ticagrelor-treated group. In addition, ticagrelor significantly decreased the ulcer-stimulated expression levels of EGF, VEGF, phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), phosphorylated P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB P65 at the ulcer margin (P<0.05). These findings suggested that ticagrelor delayed gastric ulcer healing. Furthermore, the possible mechanisms underlying the effect of ticagrelor were associated with its functions of attenuating the expression levels of VEGF and EGF, as well as suppressing the phosphorylation activation of ERK1/2, P38 and nuclear factor-κB P65. Finally, the gastric epithelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis were also inhibited.
Keywords: P2Y12 receptor antagonist; angiogenesis; cell proliferation; ulcer healing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clopidogrel delays gastric ulcer healing in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov 15;695(1-3):112-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.07.054. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22975710
-
Clopidogrel inhibits angiogenesis of gastric ulcer healing via downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.J Formos Med Assoc. 2016 Sep;115(9):764-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2015.07.022. Epub 2015 Aug 24. J Formos Med Assoc. 2016. PMID: 26315480
-
Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG enhances gastric ulcer healing in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jun 22;565(1-3):171-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.050. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17395175
-
The role of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its receptor in mucosal protection, adaptation to injury, and ulcer healing: involvement of EGF-R signal transduction pathways.J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998;27 Suppl 1:S12-20. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199800001-00004. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998. PMID: 9872493 Review.
-
Gastrointestinal mucosal regeneration: role of growth factors.Front Biosci. 1999 Mar 15;4:D303-9. doi: 10.2741/a428. Front Biosci. 1999. PMID: 10077540 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Risk of Hospitalized Bleeding of P2Y12 Inhibitors for Secondary Prophylaxis in Acute Coronary Syndrome After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Feb;113(2):412-422. doi: 10.1002/cpt.2806. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36448257 Free PMC article.
-
YQFM Alleviates Side Effects Caused by Dasatinib through the ROCK/MLC Pathway in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 29;2020:4646029. doi: 10.1155/2020/4646029. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32908560 Free PMC article.
-
An Efficient Synthetic Approach Towards Benzo[b]pyrano[2,3-e][1,4]diazepines, and Their Cytotoxic Activity.Molecules. 2020 Apr 28;25(9):2051. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092051. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32354014 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Curcumin on Radiation/Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis: Combined Meta-Analysis, Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 20;46(9):10545-10569. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090625. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antacid Therapy in Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure: Proton Pump Inhibitors vs. H2 Receptor Blockers.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Feb;38(1):181-189. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07358-4. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 35715526 Review.
References
-
- Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey DE, Jr, Ganiats TG, Holmes DR, Jr, Jaffe AS, Jneid H, Kelly RF, Kontos MC, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: A report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2014;130:e344–e426. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000134. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roffi M, Patrono C, Collet JP, Mueller C, Valgimigli M, Andreotti F, Bax JJ, Borger MA, Brotons C, Chew DP, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Task force for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-Segment elevation of the European society of cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2016;37:267–315. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv320. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
