Sophocarpine against enterovirus 71 in vitro
- PMID: 29042981
- PMCID: PMC5639281
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4958
Sophocarpine against enterovirus 71 in vitro
Abstract
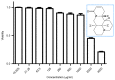
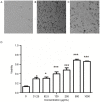
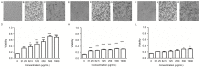
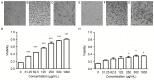
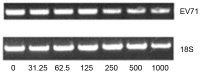
Sophocarpine (SCA) is a bioactive alkaloid present in Sophoraflavescens Ait. The present study demonstrated that SCA inhibited enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection in Vero cells. The results indicated that the 50% cytotoxicity concentration of SCA for Vero cells was 1,346 µg/ml, and the 50% inhibition concentration of SCA against EV71 was 350 µg/ml. SCA produced a marked inhibitory effect against EV71 when the Vero cells were treated with SCA prior to infection with the virus. Additionally, SCA was effective against EV71 when the Vero cells were infected with EV71 (100xTCID50) that had been treated with SCA for 2 h, and was effective when the Vero cells were infected with EV71 (100xTCID50) at 37°C under 5% CO2 for 2 h prior to treatment with SCA for 2 h. SCA was demonstrated to inhibit the attachment and penetration of EV71 and was more effective at inhibiting attachment. The assay additionally verified that SCA suppressed the replication of viral genomic RNA and indicated that SCA may inhibit EV71 infection in vitro.
Keywords: antiviral activity; cytopathic effect; enterovirus 71; sophocarpine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication and viral 3C protease by quercetin.Virol J. 2018 Jul 31;15(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-1023-6. Virol J. 2018. PMID: 30064445 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits enterovirus 71 replication by down-regulating ubiquitin-proteasome system.Virus Res. 2015 Jan 2;195:207-16. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25456405
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Inhibition of the Infectivity of Human Enterovirus 71 by a Sulfonated Food Azo Dye, Brilliant Black BN.J Virol. 2019 Aug 13;93(17):e00061-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00061-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31167919 Free PMC article.
-
The antiviral effect of 7-hydroxyisoflavone against Enterovirus 71 in vitro.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2013;15(4):382-9. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2013.770737. Epub 2013 Mar 6. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2013. PMID: 23464760
-
Antiviral activity of sophoridine against enterovirus 71 in vitro.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 23;236:124-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.02.045. Epub 2019 Mar 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30853644
Cited by
-
A review on the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicity of sophocarpine.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1353234. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1353234. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38746009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Bioevaluation of Matrine Derivatives as Potential Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Agents.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 18;15(3):436. doi: 10.3390/biom15030436. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149972 Free PMC article.
-
A computational framework of host-based drug repositioning for broad-spectrum antivirals against RNA viruses.iScience. 2021 Feb 5;24(3):102148. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102148. eCollection 2021 Mar 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33665567 Free PMC article.
-
Sophocarpine inhibits the progression of glioblastoma via PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 25;14(8):3757-3772. doi: 10.62347/SQJB1901. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39267674 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
