Immunological mechanism of low-dose priming radiation resistance in walker-256 tumor model mice
- PMID: 29042994
- PMCID: PMC5639294
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4975
Immunological mechanism of low-dose priming radiation resistance in walker-256 tumor model mice
Abstract
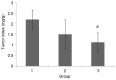
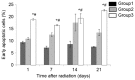
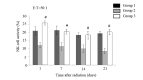
The aim of the present study was to investigate whether low-dose priming radiation induces antitumor immunity that can be augmented by the modulation of natural killer (NK) cell and cytokine activity using a mouse tumor model. Walker-256 cells were injected into the right flank of male BALB/c mice. At 7 days after inoculation, mice were divided into three groups, including group 1,2,3. In group 1 the mice were without radiation, in group 2 the mice were received 2 Gy radiation only, and in group 3 the mice were radiated with a priming dose of 75 mGy followed by 2 Gy radiation after 24 h. On day 21 following the radiation, the tumors were removed and the tumor index (tumor weight as a percentage of body weight) was calculated. At 1, 7, 14 and 21 days following the 2 Gy radiation, mouse splenocytes were isolated to analyze the NK activity and measure the production of the cytokines interleukin-1β, interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α by ELISA. Apoptosis was also measured by flow cytometry. The results demonstrated that priming radiation significantly delayed the tumor growth and prolonged the median survival time to 38 days compared with the 31-day survival in the 2 Gy radiation group. The percentage of apoptotic cells was significantly higher in the mice that received 75 mGy + 2 Gy radiation compared with that in the mice that received 2 Gy alone; by contrast, mice that were not irradiated exhibited a relatively low level of apoptosis. The primed mice had a higher level of NK activity as compared with the mice exposed to 2 Gy radiation only or mice that were not irradiated. Furthermore, cytokine expression remained at a higher level in mice receiving priming dose of radiation compared that in the mice receiving only 2 Gy radiation. In conclusion, the results indicated that low-dose priming X-ray radiation may enhance the NK activity and the levels of cytokines, and that the immune response serves an important role in anticancer therapy, including radiotherapy.
Keywords: antitumor; apoptosis; cytokines; low-dose radiation; natural killer activity; radiation resistance.
Figures
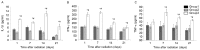
Similar articles
-
[Induction of glutathione and activation of immune functions by low-dose, whole-body irradiation with gamma-rays].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006 Oct;126(10):849-57. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.126.849. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 17016016 Review. Japanese.
-
TP53 and TP53-related genes associated with protection from apoptosis in the radioadaptive response.Radiat Res. 2007 Jan;167(1):51-7. doi: 10.1667/RR0623.1. Radiat Res. 2007. PMID: 17214514
-
[Effect of low dose heavy ion irradiation on subset percentage and cytokines expression of peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with pancreatic cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;36(6):435-9. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25241785 Chinese.
-
Low-dose total-body γ irradiation modulates immune response to acute proton radiation.Radiat Res. 2012 Mar;177(3):251-64. doi: 10.1667/rr2785.1. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 22149957
-
Radio-adaptive Response Induced by Low-dose Ionizing Radiation in Innate Immunity for Radiotherapy.Health Phys. 2023 Mar 1;124(3):166-174. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001649. Health Phys. 2023. PMID: 36719932
Cited by
-
Evidence of Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Regulation by Mitochodria-Generated Reactive Oxygen Species in RGK1 Cells.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 27;13(3):445. doi: 10.3390/biom13030445. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979380 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Results of the Effects of Localized High-Dose Radiotherapy Combined with Total Body Low-Dose Irradiation on Tumor Growth and Stimulating the Immune System in Tumor-Bearing Mice.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2023 Aug 1;13(4):323-332. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2009-1179. eCollection 2023 Aug. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2023. PMID: 37609506 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the optimal dose of low ionizing radiation to enhance immune function: a rabbit model.J Int Med Res. 2021 Aug;49(8):3000605211015079. doi: 10.1177/03000605211015079. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34369192 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
