The distribution of calbindin-D28k, parvalbumin, and calretinin immunoreactivity in the inferior colliculus of circling mouse
- PMID: 29043102
- PMCID: PMC5639178
- DOI: 10.5115/acb.2017.50.3.230
The distribution of calbindin-D28k, parvalbumin, and calretinin immunoreactivity in the inferior colliculus of circling mouse
Abstract
The circling mice with tmie gene mutation are known as an animal deafness model, which showed hyperactive circling movement. Recently, the reinvestigation of circling mouse was performed to check the inner ear pathology as a main lesion of early hearing loss. In this trial, the inner ear organs were not so damaged to cause the hearing deficit of circling (cir/cir) mouse at 18 postnatal day (P18) though auditory brainstem response data indicated hearing loss of cir/cir mice at P18. Thus, another mechanism may be correlated with the early hearing loss of cir/cir mice at P18. Hearing loss in the early life can disrupt the ascending and descending information to inferior colliculus (IC) as integration site. There were many reports that hearing loss could result in the changes in Ca2+ concentration by either cochlear ablation or genetic defect. However, little was known to be reported about the correlation between the pathology of IC and Ca2+ changes in circling mice. Therefore, the present study investigated the distribution of calcium-binding proteins (CaBPs), calbindin-D28k, parvalbumin, and calretinin immunoreactivity (IR) in the IC to compare among wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/cir), and homozygous (cir/cir) mice by immunohistochemistry. The decreases of CaBPs IR in cir/cir were statistically significant in the neurons as well as neuropil of IC. Thus, this study proposed overall distributional alteration of CaBPs IR in the IC caused by early hearing defect and might be helpful to elucidate the pathology of central auditory disorder related with Ca2+ metabolism.
Keywords: Calbindin-D28k; Calretinin; Circling mice; Inferior colliculus; Parvalbumins.
Figures
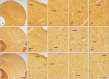
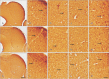

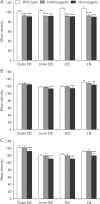
References
-
- Shin MJ, Lee JH, Yu DH, Kim BS, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Kim MO, Park C, Hyun BH, Lee S, So HS, Park R, Ryoo ZY. Ectopic expression of tmie transgene induces various recovery levels of behavior and hearing ability in the circling mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;374:17–21. - PubMed
-
- Cho KI, Lee JW, Kim KS, Lee EJ, Suh JG, Lee HJ, Kim HT, Hong SH, Chung WH, Chang KT, Hyun BH, Oh YS, Ryoo ZY. Fine mapping of the circling (cir) gene on the distal portion of mouse chromosome 9. Comp Med. 2003;53:642–648. - PubMed
-
- Chung WH, Kim KR, Cho YS, Cho DY, Woo JH, Ryoo ZY, Cho KI, Hong SH. Cochlear pathology of the circling mouse: a new mouse model of DFNB6. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007;127:244–251. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Chang SY, Jung JY, Ahn SC. Reinvestigation of cochlear pathology in circling mice. Neurosci Lett. 2015;594:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Illing RB. Activity-dependent plasticity in the adult auditory brainstem. Audiol Neurootol. 2001;6:319–345. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
