Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes predict different clinical outcomes in organ- and non-organ-confined urothelial carcinoma of the bladder following radical cystectomy
- PMID: 29043112
- PMCID: PMC5642242
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.3921
Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes predict different clinical outcomes in organ- and non-organ-confined urothelial carcinoma of the bladder following radical cystectomy
Abstract
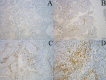
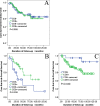
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are associated with better clinical outcomes in many tumors. TILs represent a cell-mediated immune response against the carcinoma. CD8+ TILs are a crucial component of cell-mediated immunity. The significance of CD8+ TILs has not been reported respectively in organ- and non-organ-confined urothelial carcinoma (UC) of the bladder. We explored the prognostic value of CD8+ TILs in the two groups. The presence of CD8+ TILs was assessed by immunohistochemical staining of whole tissue sections from 75 organ and 51 non-organ-confined disease patients with long-term follow-up, and its correlation with clinicopathological features and overall survival (OS) was determined. The CD8+ TIL immunohistochemical staining score was 0 (<1%), 1 (≥1%), 2 (≥5%), or 3 (≥10%) based on the percentage of positively stained cells out of total cells. A patient was considered CD8 negative if the score was 0. There were no associations between CD8+ TILs and age, sex, nuclear grade, and adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy in organ- and non-organ-confined disease. The presence of CD8+ TILs was seen more frequently in pTa-1 than pT2 stage (p = 0.033) in organ-confined disease. No associations between CD8+ TILs and pT stage, pN stage were found in non-organ-confined disease. CD8+ TILs were associated with better OS (log-rank test, P = 0.036) in non-organ-confined disease, but with poorer OS (log-rank test, P = 0.040) in organ-confined disease by the Kaplan-Meier method. In multivariate analysis, CD8+ TILs were an independent favorable prognostic factor in non-organ-confined disease, but were an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in organ-confined disease. These results suggest that CD8+ TILs have clinically significant anti-tumor activity in non-organ-confined disease, but may have pro-tumor activity in organ-confined disease. Therefore, we should be cautious if CD8+ TILs are aimed to be exploited in the treatment of bladder cancer.
Keywords: CD8+ TILs; Non-organ-confined disease; Organ-confined disease; Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of tumor PD-L1 expression combined with CD8+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in high grade serous ovarian cancer.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Nov;52:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28846888
-
CD103+ Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Predict a Favorable Prognosis in Urothelial Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder.J Urol. 2015 Aug;194(2):556-62. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.02.2941. Epub 2015 Mar 6. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25752441
-
CD8 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are predictive of survival in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 6;104(10):3967-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611618104. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360461 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Differs Depending on Lymphocyte Subsets in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 28;10:614. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00614. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32411602 Free PMC article.
-
[Prognostic factors of survival in infiltrating urothelial bladder carcinoma. A retrospective study of 158 patients treated by radical cystectomy].Bull Cancer. 1996 Feb;83(2):139-46. Bull Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8652908 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Tumor microenvironment and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer: Cytokines in the game?Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 9;9:1070383. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1070383. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36699696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiogenomic analysis of cellular tumor-stroma heterogeneity as a prognostic predictor in breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2023 Nov 25;21(1):851. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04748-6. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38007511 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic activity index and CD25+ lymphocytes predict risk of stage progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 2;15(6):e0233676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233676. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32484812 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of immunoscore related markers in bladder cancer.BMC Urol. 2022 Aug 29;22(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01085-6. BMC Urol. 2022. PMID: 36038861 Free PMC article.
-
Presence, Subtypes, and Prognostic Significance of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures in Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder.Oncologist. 2024 Feb 2;29(2):e248-e258. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad283. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 37874923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boorjian SA, Sheinin Y, Crispen PL, Farmer SA, Lohse CM, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Kwon ED, Frank I. T-cell coregulatory molecule expression in urothelial cell carcinoma: clinicopathologic correlations and association with survival. Clinical Cancer Research. 2008;14:4800–4808. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0731. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

