Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis associated with Rosai-Dorfman disease
- PMID: 29043148
- PMCID: PMC5642468
- DOI: 10.5414/CNCS108856
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis associated with Rosai-Dorfman disease
Abstract
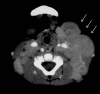
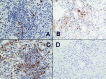
Rosai-Dorfman disease is also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. Extranodal Rosai-Dorfman disease has been reported in ~ 43% of cases; the most frequent extranodal sites - skin, soft tissue, bone, respiratory tract, and eye - are usually involved in association with lymphadenopathy. Lack of lymph node involvement is rare, especially when patients manifest renal disease. Here, we describe a patient who developed membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis when lymphadenopathy was absent. During follow-up for sinus histiocytosis, a 7-year-old Japanese boy developed proteinuria and hematuria. No renal abnormality was present in ultrasound imaging. Histologic examination of a renal biopsy specimen disclosed moderate mesangial proliferation, focal thickening of glomerular capillary walls, and mesangial interposition. Mononuclear cells infiltrated the interstitium. Immunofluorescence showed intense IgG, C3, and C4 reactivity in portions of the mesangium and glomerular capillary walls. Electron microscopy depicted nodular deposits in mesangial, endocapillary, and subepithelial areas. Immunohistochemistry for S-100 protein, CD68, and lysozyme was positive within the interstitium. CD1a staining was absent. These findings were diagnostic for membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Multidrug therapy, including methylprednisolone and mizoribine, improved urinary findings and induced complete remission of both diseases. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of Rosai-Dorfman disease complicated by renal disease in the absence of concurrent nodal involvement. Clinicians should be alert to this diagnostic possibility.
Keywords: Langerhans-cell histiocytosis; Rosai-Dorfman disease; children; cytokines; membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; mizoribine.
Figures




References
-
- Rosai J Dorfman RF Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. A newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969; 87: 63–70. - PubMed
-
- Juskevicius R Finley JL Rosai-Dorfman disease of the parotid gland: cytologic and histopathologic findings with immunohistochemical correlation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2001; 125: 1348–1350. - PubMed
-
- Foucar E Rosai J Dorfman R Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: review of entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990; 7: 19–73. - PubMed
-
- Wright DH Richards DB Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): report of a case with widespread nodal and extra nodal dissemination. Histopathology. 1981; 5: 697–709. - PubMed
-
- Kher V Gulati S Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis In: Davidson AM(ed) Oxford textbook of clinical nephrology, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford; 2005. p. 523-545.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
