Innovative strategies for a successful SLMTA country programme: The Rwanda story
- PMID: 29043189
- PMCID: PMC5637798
- DOI: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.217
Innovative strategies for a successful SLMTA country programme: The Rwanda story
Abstract
Background: In 2009, to improve the performance of laboratories and strengthen healthcare systems, the World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa (WHO AFRO) and partners launched two initiatives: a laboratory quality improvement programme called Strengthening Laboratory Management Toward Accreditation (SLMTA), and what is now called the Stepwise Laboratory Quality Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (SLIPTA).
Objectives: This study describes the achievements of Rwandan laboratories four years after the introduction of SLMTA in the country, using the SLIPTA scoring system to measure laboratory progress.
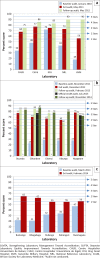
Methods: Three cohorts of five laboratories each were enrolled in the SLMTA programme in 2010, 2011 and 2013. The cohorts used SLMTA workshops, improvement projects, mentorship and quarterly performance-based financing incentives to accelerate laboratory quality improvement. Baseline, exit and follow-up audits were conducted over a two-year period from the time of enrolment. Audit scores were used to categorise laboratory quality on a scale of zero (< 55%) to five (95% - 100%) stars.
Results: At baseline, 14 of the 15 laboratories received zero stars with the remaining laboratory receiving a two-star rating. At exit, five laboratories received one star, six received two stars and four received three stars. At the follow-up audit conducted in the first two cohorts approximately one year after exit, one laboratory scored two stars, five laboratories earned three stars and four laboratories, including the National Reference Laboratory, achieved four stars.
Conclusion: Rwandan laboratories enrolled in SLMTA showed improvement in quality management systems. Sustaining the gains and further expansion of the SLMTA programme to meet country targets will require continued programme strengthening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationship(s) that may have inappropriately influenced them in writing this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comprehensive review of the SLMTA literature part 2: Measuring success.Afr J Lab Med. 2014 Nov 3;3(2):276. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.276. eCollection 2014. Afr J Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 29043201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strengthening Laboratory Management Towards Accreditation: The Lesotho experience.Afr J Lab Med. 2012 May 30;1(1):9. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v1i1.9. eCollection 2012. Afr J Lab Med. 2012. PMID: 29062729 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of SLMTA in improving laboratory quality systems in the Caribbean Region.Afr J Lab Med. 2014;3(2):199. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.199. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Afr J Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 27066396 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence from 617 laboratories in 47 countries for SLMTA-driven improvement in quality management systems.Afr J Lab Med. 2014;3(3):262. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.262. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Afr J Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 26753132 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of the SLMTA literature part 1: Content analysis and future priorities.Afr J Lab Med. 2014 Nov 3;3(2):265. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.265. eCollection 2014. Afr J Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 29043200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review of the Stepwise Laboratory Quality Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (SLIPTA) version 2:2015.Afr J Lab Med. 2020 Oct 28;9(1):1068. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v9i1.1068. eCollection 2020. Afr J Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 33240798 Free PMC article.
-
The SLMTA programme: Transforming the laboratory landscape in developing countries.Afr J Lab Med. 2014;3(3):194. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.194. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Afr J Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 26752335 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Ascent From Zero Quality to International Organization for Standardization Accreditation: A Case Study of Hai Duong Preventive Medicine Center in Vietnam, 2012-2013.Am J Clin Pathol. 2017 Apr 1;147(4):427-431. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqx017. Am J Clin Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28340123 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of the SLMTA literature part 2: Measuring success.Afr J Lab Med. 2014 Nov 3;3(2):276. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.276. eCollection 2014. Afr J Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 29043201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Referral Laboratory Personnel's Perception of Challenges and Strategies for Sustaining the Laboratory Quality Management System.Am J Clin Pathol. 2019 Nov 4;152(6):725-734. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqz092. Am J Clin Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31304959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olmsted SS, Moore RC, Meili HC, et al. . Strengthening laboratory systems in resource-limited settings. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134(3):374–380. http://dx.doi.org/10.1309/AJCPDQOSB7QR5GLR - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ravishankar N, Gubbins P, Cooley RJ, et al. . Financing of global health: Tracking development assistance for health from 1990 to 2007. Lancet. 2009;373(9681):2113–2124. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60881-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nkengasong JN, Mesele T, Orloff S, et al. . Critical role of developing national strategic plans as a guide to strengthen laboratory health systems in resource-poor settings. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;131(6):852–857. http://dx.doi.org/10.1309/AJCPC51BLOBBPAKC - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nordling L. African disease labs to get health check [published online 2009 Jul 27]. Nature.
-
- World Health Organization The Maputo declaration on strengthening of laboratory systems [document on the Internet]. c2008 [cited 2013 Jan 02]. Available from: http://www.who.int/diagnostics_laboratory/Maputo-Declaration_2008.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources