Computed tomography in children with community-acquired pneumonia
- PMID: 29043419
- PMCID: PMC5608781
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-017-3891-0
Computed tomography in children with community-acquired pneumonia
Abstract
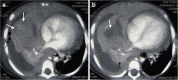
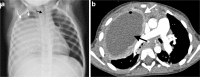
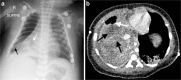
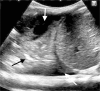
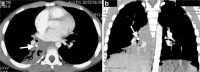
Diagnostic imaging plays a significant role in both the diagnosis and treatment of complications of pneumonia in children and chest radiography is the imaging modality of choice. Computed tomography (CT) on the other hand, is not currently a first-line imaging tool for children with suspected uncomplicated community-acquired pneumonia and is largely reserved for when complications of pneumonia are suspected or there is difficulty in differentiating pneumonia from other pathology. This review outlines the situations where CT needs to be considered in children with pneumonia, describes the imaging features of the parenchymal and pleural complications of pneumonia, discusses how CT may have a wider role in developing countries where human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and tuberculosis are prevalent, makes note of the role of CT scanning for identifying missed foreign body aspiration and, lastly, addresses radiation concerns.
Keywords: Children; Computed tomography; Empyema; Lung; Lung abscess; Necrotizing pneumonia; Pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


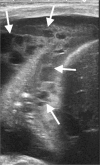
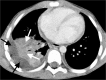

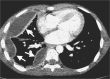
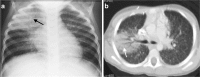

Similar articles
-
Early chest computed tomography in adult acute severe community-acquired pneumonia patients treated in the intensive care unit.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016 Sep;60(8):1102-10. doi: 10.1111/aas.12749. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016. PMID: 27272897
-
Community-Acquired Pneumonia with Negative Chest Radiography Findings: Clinical and Radiological Features.Respiration. 2019;97(6):508-517. doi: 10.1159/000495068. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Respiration. 2019. PMID: 30625485
-
[Pneumonia].Radiologe. 2017 Jan;57(1):4-5. doi: 10.1007/s00117-016-0204-9. Radiologe. 2017. PMID: 28101626 German. No abstract available.
-
[Community-acquired pneumonia].Radiologe. 2017 Jan;57(1):6-12. doi: 10.1007/s00117-016-0199-2. Radiologe. 2017. PMID: 28054135 Review. German.
-
Radiology of pneumonia.Clin Chest Med. 1999 Sep;20(3):549-62. doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(05)70235-5. Clin Chest Med. 1999. PMID: 10516903 Review.
Cited by
-
[Imaging of Acute Pulmonary and Airway Diseases in Children].Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi. 2020 Jul;81(4):756-769. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2020.81.4.756. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi. 2020. PMID: 36238171 Free PMC article. Review. Korean.
-
Radiologic Diagnosis and Hospitalization among Children with Severe Community Acquired Pneumonia: A Prospective Cohort Study.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jan 9;2019:6202405. doi: 10.1155/2019/6202405. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30729128 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of standardizing fibrinolytic therapy for parapneumonic effusion.Pediatr Radiol. 2022 Nov;52(12):2413-2420. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05365-z. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Pediatr Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35451632 Free PMC article.
-
Point-of-care lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of childhood pneumonia.Lung India. 2024 Nov 1;41(6):411-415. doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_574_23. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Lung India. 2024. PMID: 39465919 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional analysis using low-dose computed tomography to evaluate the severity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Mar 1;13(3):1874-1886. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-508. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36915342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris M, Clark J, Coote N et al (2011) British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in children: update 2011. Thorax 66 Suppl 2:ii1-23 - PubMed
-
- Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, et al. The management of community-acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:e25–e76. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir531. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

