Mapping DNA Breaks by Next-Generation Sequencing
- PMID: 29043624
- PMCID: PMC8057127
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7306-4_13
Mapping DNA Breaks by Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
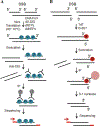
Here, we present two approaches to map DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and single-strand breaks (SSBs) in the genome of human cells. We named these methods respectively DSB-Seq and SSB-Seq. We tested the DSB and SSB-Seq in HCT1116, human colon cancer cells, and validated the results using the topoisomerase 2 (Top2)-poisoning agent etoposide (ETO). These methods are powerful tools for the direct detection of the physiological and pathological "breakome" of the DNA in human cells.
Keywords: DNA damage; Double-strand breaks (DSBs); Etoposide (ETO); Single-strand breaks (SSBs); Topoisomerase 2 (Top2).
Figures

References
-
- Blitzblau HG, Hochwagen A (2011) Genome-wide detection of meiotic DNA double-strand break hotspots using single-stranded DNA. Methods Mol Biol 745:47–63 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

