Emissive Synthetic Cofactors: An Isomorphic, Isofunctional, and Responsive NAD+ Analogue
- PMID: 29043790
- PMCID: PMC5766281
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b05852
Emissive Synthetic Cofactors: An Isomorphic, Isofunctional, and Responsive NAD+ Analogue
Abstract
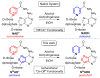
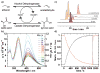
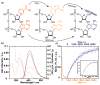
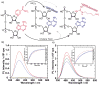
The synthesis, photophysics, and biochemical utility of a fluorescent NAD+ analogue based on an isothiazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidine core (NtzAD+) are described. Enzymatic reactions, photophysically monitored in real time, show NtzAD+ and NtzADH to be substrates for yeast alcohol dehydrogenase and lactate dehydrogenase, respectively, with reaction rates comparable to that of the native cofactors. A drop in fluorescence is seen as NtzAD+ is converted to NtzADH, reflecting a complementary photophysical behavior to that of the native NAD+/NADH. NtzAD+ and NtzADH serve as substrates for NADase, which selectively cleaves the nicotinamide's glycosidic bond yielding tzADP-ribose. NtzAD+ also serves as a substrate for ribosyl transferases, including human adenosine ribosyl transferase 5 (ART5) and Cholera toxin subunit A (CTA), which hydrolyze the nicotinamide and transfer tzADP-ribose to an arginine analogue, respectively. These reactions can be monitored by fluorescence spectroscopy, in stark contrast to the corresponding processes with the nonemissive NAD+.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Yitzhak Tor provides consulting services to TriLink Biotechnologies. The terms of the arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures
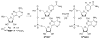
Similar articles
-
Isomorphic Fluorescent Nucleosides.Acc Chem Res. 2024 May 7;57(9):1325-1335. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00042. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38613490 Free PMC article.
-
Emissive Synthetic Cofactors: Enzymatic Interconversions of tz A Analogues of ATP, NAD+ , NADH, NADP+ , and NADPH.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Jan 22;57(4):1087-1090. doi: 10.1002/anie.201711935. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29228460 Free PMC article.
-
Emissive Synthetic Cofactors: A Highly Responsive NAD+ Analogue Reveals Biomolecular Recognition Features.Chemistry. 2019 Mar 21;25(17):4379-4389. doi: 10.1002/chem.201805520. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Chemistry. 2019. PMID: 30648291 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins: unveiling the secrets of a crucial regulatory mechanism in mammalian cells.Ann Med. 2006;38(3):188-99. doi: 10.1080/07853890600655499. Ann Med. 2006. PMID: 16720433 Review.
-
NAD hydrolysis: chemical and enzymatic mechanisms.Mol Cell Biochem. 1994 Sep;138(1-2):245-51. doi: 10.1007/BF00928468. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7898470 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzymatic Syntheses and Applications of Fluorescent Cyclic Dinucleotides.Chemistry. 2020 May 12;26(27):6076-6084. doi: 10.1002/chem.202001194. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 32157755 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the cofactor specificity of wild-type phosphite dehydrogenase and its mutant using molecular dynamics simulations.RSC Adv. 2021 Apr 19;11(24):14527-14533. doi: 10.1039/d1ra00221j. eCollection 2021 Apr 15. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35424015 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescing Isofunctional Ribonucleosides: Assessing Adenosine Deaminase Activity and Inhibition.Chembiochem. 2019 Mar 1;20(5):718-726. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201800665. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Chembiochem. 2019. PMID: 30566279 Free PMC article.
-
Isomorphic Fluorescent Nucleosides.Acc Chem Res. 2024 May 7;57(9):1325-1335. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00042. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38613490 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalised Cofactor Mimics for Interactome Discovery and Beyond.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Jul 18;61(29):e202201136. doi: 10.1002/anie.202201136. Epub 2022 May 31. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 35286003 Free PMC article. Review.

