Bilateral disc drusen in a diabetic patient simulating diabetic papillopathy as a cause of disc edema
- PMID: 29044087
- PMCID: PMC5678315
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_355_17
Bilateral disc drusen in a diabetic patient simulating diabetic papillopathy as a cause of disc edema
Abstract
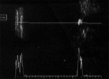
Bilateral optic disc edema in a diabetic patient may be caused by diabetic papillopathy. We herein report on a patient with bilateral optic disc drusen simulating diabetic papillopathy. A 55-year-old patient with type 2 diabetes presented with decreased vision of 1-month. Diabetic papillopathy was initially considered as there was disc edema in both eyes with focal hemorrhages at the disc margin and mild visual loss. Ultrasound of the optic nerve head revealed optic disc drusen in both eyes and this was also confirmed by the control photograph. Optic nerve head drusen should be considered in the differential diagnosis of a diabetic patient presenting with disc edema.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pavan PR, Aiello LM, Wafai MZ, Briones JC, Sebestyen JG, Bradbury MJ, et al. Optic disc edema in juvenile-onset diabetes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980;98:2193–5. - PubMed
-
- Lubow M, Makley TA., Jr Pseudopapilledema of juvenile diabetes mellitus. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971;85:417–22. - PubMed
-
- Bayraktar Z, Alacali N, Bayraktar S. Diabetic papillopathy in type II diabetic patients. Retina. 2002;22:752–8. - PubMed
-
- Regillo CD, Brown GC, Savino PJ, Byrnes GA, Benson WE, Tasman WS, et al. Diabetic papillopathy. Patient characteristics and fundus findings. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995;113:889–95. - PubMed
-
- Inoue M, Tsukahara Y. Vascular optic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1997;41:328–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical