DNA-binding of the Tet-transactivator curtails antigen-induced lymphocyte activation in mice
- PMID: 29044097
- PMCID: PMC5647323
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01022-4
DNA-binding of the Tet-transactivator curtails antigen-induced lymphocyte activation in mice
Abstract
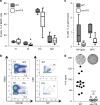
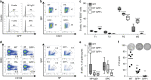
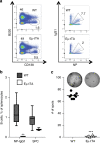
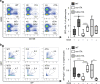
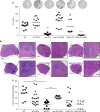
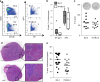
The Tet-On/Off system for conditional transgene expression constitutes state-of-the-art technology to study gene function by facilitating inducible expression in a timed and reversible manner. Several studies documented the suitability and versatility of this system to trace lymphocyte fate and to conditionally express oncogenes or silence tumour suppressor genes in vivo. Here, we show that expression of the tetracycline/doxycycline-controlled Tet-transactivator, while tolerated well during development and in immunologically unchallenged animals, impairs the expansion of antigen-stimulated T and B cells and thereby curtails adaptive immune responses in vivo. Transactivator-mediated cytotoxicity depends on DNA binding, but can be overcome by BCL2 overexpression, suggesting that apoptosis induction upon lymphocyte activation limits cellular and humoral immune responses. Our findings suggest a possible system-intrinsic biological bias of the Tet-On/Off system in vivo that will favour the outgrowth of apoptosis resistant clones, thus possibly confounding data published using such systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Tetracycline-Controlled Transactivator (Tet-On/Off) System in β-Cells Reduces Insulin Expression and Secretion in Mice.Diabetes. 2021 Dec;70(12):2850-2859. doi: 10.2337/db21-0147. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34610983 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-A*0201-restricted cytolytic responses to the rtTA transactivator dominant and cryptic epitopes compromise transgene expression induced by the tetracycline on system.Mol Ther. 2004 Aug;10(2):279-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.05.012. Mol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15294175
-
Improved Tet-On and Tet-Off systems for tetracycline-regulated expression of genes in Candida.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):303-316. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0720-9. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28597304
-
Immune responses against tetracycline-dependent transactivators affect long-term expression of mouse erythropoietin delivered by a helper-dependent adenoviral vector.J Gene Med. 2005 Aug;7(8):1086-96. doi: 10.1002/jgm.758. J Gene Med. 2005. PMID: 15772935
-
Improved applications of the tetracycline-regulated gene depletion system.Biosci Trends. 2009 Oct;3(5):161-7. Biosci Trends. 2009. PMID: 20103842 Review.
Cited by
-
Correspondence: T cells are compromised in tetracycline transactivator transgenic mice.Cell Death Differ. 2018 Mar;25(3):634-636. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0042-y. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Cell Death Differ. 2018. PMID: 29352266 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Tetracycline response element driven Cre causes ectopic recombinase activity independent of transactivator element.Mol Metab. 2022 Jul;61:101501. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101501. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Mol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35452876 Free PMC article.
-
The Tetracycline-Controlled Transactivator (Tet-On/Off) System in β-Cells Reduces Insulin Expression and Secretion in Mice.Diabetes. 2021 Dec;70(12):2850-2859. doi: 10.2337/db21-0147. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34610983 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Relevant and Immune Deficient Mice: Options and Opportunities in Translational Research.ILAR J. 2018 Dec 31;59(3):211-246. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ily026. ILAR J. 2018. PMID: 31197363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

