A review of wheat diseases-a field perspective
- PMID: 29045052
- PMCID: PMC6638159
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12618
A review of wheat diseases-a field perspective
Abstract
Wheat is one of the primary staple foods throughout the planet. Significant yield gains in wheat production over the past 40 years have resulted in a steady balance of supply versus demand. However, predicted global population growth rates and dietary changes mean that substantial yield gains over the next several decades will be needed to meet this escalating demand. A key component to meeting this challenge is better management of fungal incited diseases, which can be responsible for 15%-20% yield losses per annum. Prominent diseases of wheat that currently contribute to these losses include the rusts, blotches and head blight/scab. Other recently emerged or relatively unnoticed diseases, such as wheat blast and spot blotch, respectively, also threaten grain production. This review seeks to provide an overview of the impact, distribution and management strategies of these diseases. In addition, the biology of the pathogens and the molecular basis of their interaction with wheat are discussed.
Keywords: Fusarium head blight/scab; Helminthosporium; Magnaporthe; blotch; fungal pathogens; rusts; wheat diseases.
© 2017 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures

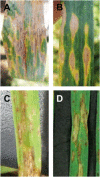

References
-
- Ali, S. , Gladieux, P. , Leconte, M. , Gautier, A. , Justesen, A.F. , Hovmøller, M.S. , Enjalbert, J. and de Vallavieille‐Pope, C. (2014) Origin, migration routes and worldwide population genetic structure of the wheat yellow rust pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici . PLoS Pathog. 10, e1003903. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anh, V.L. , Anh, N.T. , Tagle, A.G. , Vy, T.T.P. , Inoue, Y. , Takumi, S. , Chuma, I. and Tosa, Y. (2015) Rmg8, a new gene for resistance to Triticum isolates of Pyricularia oryzae in hexaploid wheat. Phytopathology, 105, 1568–1572. - PubMed
-
- Anikster, Y. , Bushnell, W. , Roelfs, A. , Eilam, T. and Manisterski, J. (1997) Puccinia recondita causing leaf rust on cultivated wheats, wild wheats, and rye. Can. J. Bot. 75, 2082–2096.
-
- Anonymous . (2017) Of rice and men. A circular tale of changing food preferences The Economist, Print Edition, International.
-
- Antoni, E.A. , Rybak, K. , Tucker, M.P. , Hane, J.K. , Solomon, P.S. , Drenth, A. , Shankar, M. and Oliver, R.P. (2010) Ubiquity of ToxA and absence of ToxB in Australian populations of Pyrenophora tritici‐repentis . Austral. Plant Pathol. 39, 63–68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- BB/J/00426X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I000488/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/P016855/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/K020056/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J/004383/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

