SELECT-2: a phase II, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy of selumetinib plus docetaxel as a second-line treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29045535
- PMCID: PMC5834012
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdx628
SELECT-2: a phase II, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy of selumetinib plus docetaxel as a second-line treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Combination of selumetinib plus docetaxel provided clinical benefit in a previous phase II trial for patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The phase II SELECT-2 trial investigated safety and efficacy of selumetinib plus docetaxel for patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC.
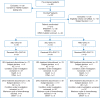
Patients and methods: Patients who had disease progression after first-line anti-cancer therapy were randomized (2 : 2 : 1) to selumetinib 75 mg b.i.d. plus docetaxel 60 or 75 mg/m2 (SEL + DOC 60; SEL + DOC 75), or placebo plus docetaxel 75 mg/m2 (PBO + DOC 75). Patients were initially enrolled independently of KRAS mutation status, but the protocol was amended to include only patients with centrally confirmed KRAS wild-type NSCLC. Primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS; RECIST 1.1); statistical analyses compared each selumetinib group with PBO + DOC 75 for KRAS wild-type and overall (KRAS mutant or wild-type) populations.
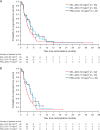
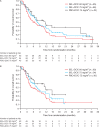
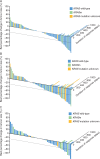
Results: A total of 212 patients were randomized; 69% were KRAS wild-type. There were no statistically significant improvements in PFS or overall survival for overall or KRAS wild-type populations in either selumetinib group compared with PBO + DOC 75. Overall population median PFS for SEL + DOC 60, SEL + DOC 75 compared with PBO + DOC 75 was 3.0, 4.2, and 4.3 months, HRs: 1.12 (90% CI: 0.8, 1.61) and 0.92 (90% CI: 0.65, 1.31), respectively. In the overall population, a higher objective response rate (ORR; investigator assessed) was observed for SEL + DOC 75 (33%) compared with PBO + DOC 75 (14%); odds ratio: 3.26 (90% CI: 1.47, 7.95). Overall the tolerability profile of SEL + DOC was consistent with historical data, without new or unexpected safety concerns identified.
Conclusion: The primary end point (PFS) was not met. The higher ORR with SEL + DOC 75 did not translate into prolonged PFS for the overall or KRAS wild-type patient populations. No clinical benefit was observed with SEL + DOC in KRAS wild-type patients compared with docetaxel alone. No unexpected safety concerns were reported.
Trial identifier: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT01750281.
Keywords: KRAS; MEK1/2; advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC); docetaxel; metastatic disease; selumetinib.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selumetinib Plus Docetaxel Compared With Docetaxel Alone and Progression-Free Survival in Patients With KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The SELECT-1 Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2017 May 9;317(18):1844-1853. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.3438. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28492898 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Selumetinib plus docetaxel for KRAS-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jan;14(1):38-47. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70489-8. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Lancet Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23200175 Clinical Trial.
-
Study Design and Rationale for a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Selumetinib in Combination With Docetaxel as Second-Line Treatment in Patients With KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (SELECT-1).Clin Lung Cancer. 2016 Mar;17(2):e1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.12.010. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Clin Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26837474 Clinical Trial.
-
Selumetinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Aug;26(8):973-984. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1351543. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28675058 Review.
-
Selumetinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2016 Nov;12(22):2545-2560. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0132. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27467210 Review.
Cited by
-
MEK inhibitors for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jan 5;14(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01025-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33402199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Factors and Markers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Recent Progress and Future Challenges.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 4;14(10):1906. doi: 10.3390/genes14101906. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of selumetinib as secondary therapy for late-stage and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: results from a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 May;10(10):593. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1849. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35722363 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Gene Signature for Squamous Cell Carcinoma with a Higher Risk for Treatment Failure and Accelerated MEK-ERK Pathway Activity.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 15;13(20):5182. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205182. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680330 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Evaluation of Single Nucleotide Variants by Two Different Technologies in Paraffin Samples of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Nov 3;10(11):902. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110902. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33153192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA. et al. Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13(5): 1576–1583. - PubMed
-
- Banerji U, Camidge DR, Verheul HM. et al. The first-in-human study of the hydrogen sulfate (Hyd-sulfate) capsule of the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886): a phase I open-label multicenter trial in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16(5): 1613–1623. - PubMed
-
- Roberts PJ, Stinchcombe TE.. KRAS mutation: should we test for it, and does it matter? J Clin Oncol 2013; 31(8): 1112–1121. - PubMed
-
- Davies BR, Logie A, McKay JS. et al. AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther 2007; 6(8): 2209–2219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

