HpARI Protein Secreted by a Helminth Parasite Suppresses Interleukin-33
- PMID: 29045903
- PMCID: PMC5655542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.09.015
HpARI Protein Secreted by a Helminth Parasite Suppresses Interleukin-33
Abstract
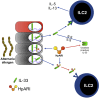
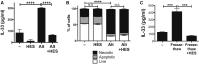
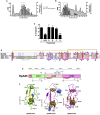
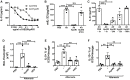
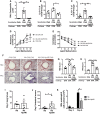
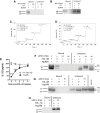
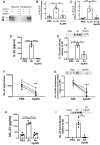
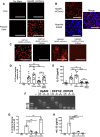
Infection by helminth parasites is associated with amelioration of allergic reactivity, but mechanistic insights into this association are lacking. Products secreted by the mouse parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus suppress type 2 (allergic) immune responses through interference in the interleukin-33 (IL-33) pathway. Here, we identified H. polygyrus Alarmin Release Inhibitor (HpARI), an IL-33-suppressive 26-kDa protein, containing three predicted complement control protein (CCP) modules. In vivo, recombinant HpARI abrogated IL-33, group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) and eosinophilic responses to Alternaria allergen administration, and diminished eosinophilic responses to Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, increasing parasite burden. HpARI bound directly to both mouse and human IL-33 (in the cytokine's activated state) and also to nuclear DNA via its N-terminal CCP module pair (CCP1/2), tethering active IL-33 within necrotic cells, preventing its release, and forestalling initiation of type 2 allergic responses. Thus, HpARI employs a novel molecular strategy to suppress type 2 immunity in both infection and allergy.
Keywords: IL-33; allergy; asthma; helminth; immunomodulation; parasite.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bessa J., Meyer C.A., de Vera Mudry M.C., Schlicht S., Smith S.H., Iglesias A., Cote-Sierra J. Altered subcellular localization of IL-33 leads to non-resolving lethal inflammation. J. Autoimmun. 2014;55:33–41. - PubMed
-
- Blein S., Ginham R., Uhrin D., Smith B.O., Soares D.C., Veltel S., McIlhinney R.A., White J.H., Barlow P.N. Structural analysis of the complement control protein (CCP) modules of GABA(B) receptor 1a: only one of the two CCP modules is compactly folded. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:48292–48306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

