Neonatal Colonic Inflammation Increases Spinal Transmission and Cystathionine β-Synthetase Expression in Spinal Dorsal Horn of Rats with Visceral Hypersensitivity
- PMID: 29046639
- PMCID: PMC5632648
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00696
Neonatal Colonic Inflammation Increases Spinal Transmission and Cystathionine β-Synthetase Expression in Spinal Dorsal Horn of Rats with Visceral Hypersensitivity
Abstract
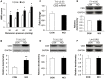
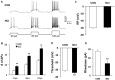
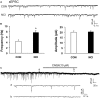
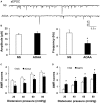
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain and alteration of bowel movements. The pathogenesis of visceral hypersensitivity in IBS patients remains largely unknown. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is reported to play an important role in development of visceral hyperalgesia. However, the role of H2S at spinal dorsal horn level remains elusive in visceral hypersensitivity. The aim of this study is designed to investigate how H2S takes part in visceral hypersensitivity of adult rats with neonatal colonic inflammation (NCI). Visceral hypersensitivity was induced by neonatal colonic injection of diluted acetic acid. Expression of an endogenous H2S synthesizing enzyme cystathionine β-synthetase (CBS) was determined by Western blot. Excitability and synaptic transmission of neurons in the substantia gelatinosa (SG) of spinal cord was recorded by patch clamping. Here, we showed that expression of CBS in the spinal dorsal horn was significantly upregulated in NCI rats. The frequency of glutamatergic synaptic activities in SG was markedly enhanced in NCI rats when compared with control rats. Application of NaHS increased the frequency of both spontaneous and miniature excitatory post-synaptic currents of SG neurons in control rats through a presynaptic mechanism. In contrast, application of AOAA, an inhibitor of CBS, dramatically suppressed the frequency of glutamatergic synaptic activities of SG neurons of NCI rats. Importantly, intrathecal injection of AOAA remarkably attenuated visceral hypersensitivity of NCI rats. These results suggest that H2S modulates pain signaling likely through a presynaptic mechanism in SG of spinal dorsal horn, thus providing a potential therapeutic strategy for treatment for chronic visceral pain in patients with IBS.
Keywords: excitatory post-synaptic current; hydrogen sulfide; irritable bowel syndrome; spinal cord dorsal horn; visceral pain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neonatal colonic inflammation sensitizes voltage-gated Na(+) channels via upregulation of cystathionine β-synthetase expression in rat primary sensory neurons.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 May 1;304(9):G763-72. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00466.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23449670
-
The endogenous hydrogen sulfide producing enzyme cystathionine-beta synthase contributes to visceral hypersensitivity in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome.Mol Pain. 2009 Aug 6;5:44. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-44. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 19660142 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenergic stimulation sensitizes TRPV1 through upregulation of cystathionine β-synthetase in a rat model of visceral hypersensitivity.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 3;5:16109. doi: 10.1038/srep16109. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26527188 Free PMC article.
-
[Role of hydrogen sulfide, a gasotransmitter, in colonic pain and inflammation].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014;134(12):1245-52. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.14-00209-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 25452234 Review. Japanese.
-
The efficacy and neural mechanism of acupuncture therapy in the treatment of visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome.Front Neurosci. 2023 Sep 4;17:1251470. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1251470. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37732301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting spinal TRAF6 expression attenuates chronic visceral pain in adult rats with neonatal colonic inflammation.Mol Pain. 2020 Jan-Dec;16:1744806920918059. doi: 10.1177/1744806920918059. Mol Pain. 2020. PMID: 32299285 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of BK channels attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity in an IBS-like rat model.Mol Pain. 2021 Jan-Dec;17:17448069211040364. doi: 10.1177/17448069211040364. Mol Pain. 2021. PMID: 34407673 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting GATA1 and p2x7r Locus Binding in Spinal Astrocytes Suppresses Chronic Visceral Pain by Promoting DNA Demethylation.Neurosci Bull. 2022 Apr;38(4):359-372. doi: 10.1007/s12264-021-00799-1. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Neurosci Bull. 2022. PMID: 34890016 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of homocysteine-mediated endothelial injury and its consequences for atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 16;9:1109445. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1109445. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36727029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Folic acid attenuates chronic visceral pain by reducing clostridiales abundance and hydrogen sulfide production.Mol Pain. 2023 Jan-Dec;19:17448069221149834. doi: 10.1177/17448069221149834. Mol Pain. 2023. PMID: 36550612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Distrutti E., Sediari L., Mencarelli A., Renga B., Orlandi S., Russo G., et al. (2006b). 5-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid 4-(5-thioxo-5H-[1,2]dithiol-3yl)-phenyl ester (ATB-429), a hydrogen sulfide-releasing derivative of mesalamine, exerts antinociceptive effects in a model of postinflammatory hypersensitivity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319 447–458. 10.1124/jpet.106.106435 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

