Therapeutic Antibodies: What Have We Learnt from Targeting CD20 and Where Are We Going?
- PMID: 29046676
- PMCID: PMC5632755
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01245
Therapeutic Antibodies: What Have We Learnt from Targeting CD20 and Where Are We Going?
Abstract
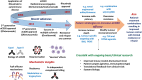
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have become one of the fastest growing classes of drugs in recent years and are approved for the treatment of a wide range of indications, from cancer to autoimmune disease. Perhaps the best studied target is the pan B-cell marker CD20. Indeed, the first mAb to receive approval by the Food and Drug Administration for use in cancer treatment was the CD20-targeting mAb rituximab (Rituxan®). Since its approval for relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in 1997, rituximab has been licensed for use in the treatment of numerous other B-cell malignancies, as well as autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis. Despite having a significant impact on the treatment of these patients, the exact mechanisms of action of rituximab remain incompletely understood. Nevertheless, numerous second- and third-generation anti-CD20 mAbs have since been developed using various strategies to enhance specific effector functions thought to be key for efficacy. A plethora of knowledge has been gained during the development and testing of these mAbs, and this knowledge can now be applied to the design of novel mAbs directed to targets beyond CD20. As we enter the "post-rituximab" era, this review will focus on the lessons learned thus far through investigation of anti-CD20 mAb. Also discussed are current and future developments relating to enhanced effector function, such as the ability to form multimers on the target cell surface. These strategies have potential applications not only in oncology but also in the improved treatment of autoimmune disorders and infectious diseases. Finally, potential approaches to overcoming mechanisms of resistance to anti-CD20 therapy are discussed, chiefly involving the combination of anti-CD20 mAbs with various other agents to resensitize patients to treatment.
Keywords: Fc engineering; Fc gamma receptors; anti-CD20; combination therapies; isotype; monoclonal antibody; resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood (2010) 116(12):2040–5. 10.1182/blood-2010-03-276246 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

