Overexpression of NPR1 in Brassica juncea Confers Broad Spectrum Resistance to Fungal Pathogens
- PMID: 29046679
- PMCID: PMC5632730
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01693
Overexpression of NPR1 in Brassica juncea Confers Broad Spectrum Resistance to Fungal Pathogens
Abstract
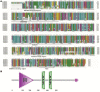
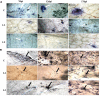
Brassica juncea (Indian mustard) is a commercially important oil seed crop, which is highly affected by many biotic stresses. Among them, Alternaria leaf blight and powdery mildew are the most devastating diseases leading to huge yield losses in B. juncea around the world. In this regard, genetic engineering is a promising tool that may possibly allow us to enhance the B. juncea disease resistance against these pathogens. NPR1 (non-expressor of pathogen-related gene 1) is a bonafide receptor of salicylic acid (SA) which modulates multiple immune responses in plants especially activation of induced and systemic acquired resistance (SAR). Here, we report the isolation and characterization of new NPR1 homolog (BjNPR1) from B. juncea. The phylogenetic tree constructed based on the deduced sequence of BjNPR1 with homologs from other species revealed that BjNPR1 grouped together with other known NPR1 proteins of Cruciferae family, and was nearest to B. napus. Furthermore, expression analysis showed that BjNPR1 was upregulated after SA treatment and fungal infection but not by jasmonic acid or abscisic acid. To understand the defensive role of this gene, we generated B. juncea transgenic lines overexpressing BjNPR1, and further confirmed by PCR and Southern blotting. The transgenic lines showed no phenotypic abnormalities, and constitutive expression of BjNPR1 activates defense signaling pathways by priming the expression of antifungal PR genes. Moreover, BjNPR1 transgenic lines showed enhanced resistance to Alternaria brassicae and Erysiphe cruciferarum as there was delay in symptoms and reduced disease severity than non-transgenic plants. In addition, the rate of disease spreading to uninfected or distal parts was also delayed in transgenic plants thus suggesting the activation of SAR. Altogether, the present study suggests that BjNPR1 is involved in broad spectrum of disease resistance against fungal pathogens.
Keywords: Alternaria; Brassica juncea; NPR1; Powdery mildew; jasmonic acid; salicylic acid; systemic acquired resistance.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Overexpression of flowering locus D (FLD) in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) enhances tolerance to Alternaria brassicae and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.Plant Cell Rep. 2023 Jul;42(7):1233-1250. doi: 10.1007/s00299-023-03021-w. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Plant Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37119284
-
Transgenic indica rice lines, expressing Brassica juncea Nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes 1 (BjNPR1), exhibit enhanced resistance to major pathogens.J Biotechnol. 2013 Jul 10;166(3):114-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.04.016. Epub 2013 May 9. J Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23664883
-
Transgenic pearl millet male fertility restorer line (ICMP451) and hybrid (ICMH451) expressing Brassica juncea Nonexpressor of pathogenesis related genes 1 (BjNPR1) exhibit resistance to downy mildew disease.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 6;9(6):e90839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090839. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24603762 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of broad-spectrum disease resistance in wheat through key genes involved in systemic acquired resistance.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 23;15:1355178. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1355178. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38463563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Status of the Disease-Resistant Gene(s)/QTLs, and Strategies for Improvement in Brassica juncea.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 3;12:617405. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.617405. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33747001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-induced proteins enhance thermal endurance in soil bacterium Priestia aryabhattai strain PSK.N2.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 Jul 2;118(8):102. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02118-4. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40601179
-
Overexpression of Ginkbilobin-2 homologous domain gene improves tolerance to Phytophthora cinnamomi in somatic embryos of Quercus suber.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 21;14(1):19357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70272-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39169119 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Microbiome: An Ocean of Possibilities for Improving Disease Resistance in Plants.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 3;11(2):392. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020392. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A dominant gene Ihrl1 is tightly linked to and inhibits the gene Ndhrl1 mediating nitrogen-dependent hypersensitive reaction-like phenotype in wheat.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Oct;135(10):3563-3570. doi: 10.1007/s00122-022-04200-1. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 36030437
-
Plant Defense Stimulator Mediated Defense Activation Is Affected by Nitrate Fertilization and Developmental Stage in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2020 May 26;11:583. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00583. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32528493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali S., Chandrashekar N., Rawat S., Nayanakantha N. M. C., Mir Z. A., Manoharan A., et al. (2017). Isolation and molecular characterization of pathogenesis related PR2 gene and its promoter from Brassica juncea. Biol. Plant. 61 763–773. 10.1007/s10535-017-0726-7 - DOI
-
- Bairwa S. K., Godara S. L., Meena S. (2015). In vitro efficacy of fungicides on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and their potential for control of stem rot in Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Int. J. Bioresour. Stress Manage. 6 497–502. 10.5958/0976-4038.2015.00073.1 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

