The Diversity of Sequence and Chromosomal Distribution of New Transposable Element-Related Segments in the Rye Genome Revealed by FISH and Lineage Annotation
- PMID: 29046683
- PMCID: PMC5632726
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01706
The Diversity of Sequence and Chromosomal Distribution of New Transposable Element-Related Segments in the Rye Genome Revealed by FISH and Lineage Annotation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: The Diversity of Sequence and Chromosomal Distribution of New Transposable Element-Related Segments in the Rye Genome Revealed by FISH and Lineage Annotation.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Nov 21;8:2020. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02020. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29206242 Free PMC article.
Abstract
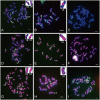
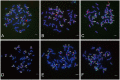
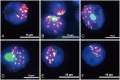
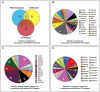
Transposable elements (TEs) in plant genomes exhibit a great variety of structure, sequence content and copy number, making them important drivers for species diversity and genome evolution. Even though a genome-wide statistic summary of TEs in rye has been obtained using high-throughput DNA sequencing technology, the accurate diversity of TEs in rye, as well as their chromosomal distribution and evolution, remains elusive due to the repetitive sequence assembling problems and the high dynamic and nested nature of TEs. In this study, using genomic plasmid library construction combined with dot-blot hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis, we successfully isolated 70 unique FISH-positive TE-related sequences including 47 rye genome specific ones: 30 showed homology or partial homology with previously FISH characterized sequences and 40 have not been characterized. Among the 70 sequences, 48 sequences carried Ty3/gypsy-derived segments, 7 sequences carried Ty1/copia-derived segments and 15 sequences carried segments homologous with multiple TE families. 26 TE lineages were found in the 70 sequences, and among these lineages, Wilma was found in sequences dispersed in all chromosome regions except telomeric positions; Abiba was found in sequences predominantly located at pericentromeric and centromeric positions; Wis, Carmilla, and Inga were found in sequences displaying signals dispersed from distal regions toward pericentromeric positions; except DNA transposon lineages, all the other lineages were found in sequences displaying signals dispersed from proximal regions toward distal regions. A high percentage (21.4%) of chimeric sequences were identified in this study and their high abundance in rye genome suggested that new TEs might form through recombination and nested transposition. Our results also gave proofs that diverse TE lineages were arranged at centromeric and pericentromeric positions in rye, and lineages like Abiba might play a role in their structural organization and function. All these results might help in understanding the diversity and evolution of TEs in rye, as well as their driving forces in rye genome organization and evolution.
Keywords: Secale cereale; TE lineages; fluoresence in situ hybridization; nested transposition; variation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosomal distribution and evolution of abundant retrotransposons in plants: gypsy elements in diploid and polyploid Brachiaria forage grasses.Chromosome Res. 2015 Sep;23(3):571-82. doi: 10.1007/s10577-015-9492-6. Chromosome Res. 2015. PMID: 26386563
-
Corrigendum: The Diversity of Sequence and Chromosomal Distribution of New Transposable Element-Related Segments in the Rye Genome Revealed by FISH and Lineage Annotation.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Nov 21;8:2020. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02020. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29206242 Free PMC article.
-
Superior: a novel repetitive DNA element dispersed in the rye genome.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009;125(4):306-20. doi: 10.1159/000235937. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19864894
-
Do Ty3/Gypsy Transposable Elements Play Preferential Roles in Sex Chromosome Differentiation?Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;12(4):522. doi: 10.3390/life12040522. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of retrotransposon-derived genetic markers to analyse genomic variability in plants.Funct Plant Biol. 2018 Jan;46(1):15-29. doi: 10.1071/FP18098. Funct Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30939255 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary convergence or homology? Comparative cytogenomics of Caesalpinia group species (Leguminosae) reveals diversification in the pericentromeric heterochromatic composition.Planta. 2019 Dec;250(6):2173-2186. doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03287-z. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Planta. 2019. PMID: 31696317
-
The distribution pattern of 5-methylcytosine in rye (Secale L.) chromosomes.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 15;15(10):e0240869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240869. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33057421 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Sequencing Crested Wheatgrass Chromosomes Identified Evolutionary Structural Changes and Genes and Facilitated the Development of SSR Markers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 16;23(6):3191. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063191. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328613 Free PMC article.
-
Copy Number Variation of Transposable Elements in Thinopyrum intermedium and Its Diploid Relative Species.Plants (Basel). 2019 Dec 21;9(1):15. doi: 10.3390/plants9010015. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31877707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appels R., Driscoll C., Peacock W. (1978). Heterochromatin and highly repeated DNA sequences in rye (Secale cereale). Chromosoma 70 67–89. 10.1007/BF00292217 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

