Effect of methanol extract of Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic mice
- PMID: 29046711
- PMCID: PMC5640945
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-017-0150-0
Effect of methanol extract of Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic mice
Abstract
Background: The dried root of Salvia miltiorrhiza, Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix (SR), is one of the most popular medicinal herbs in Asian countries such as China and Korea. In Asian traditional medicine, SR is considered to have a bitter flavor, be slightly cold in nature, and exert therapeutic actions in the heart and liver meridians. Thus, SR has been used to control symptoms related to cardiovascular diseases. Hyperlipidemia is recognized as the main cause of cerebrovascular and heart diseases; consequently, therapeutic strategies for hyperlipidemia have been widely studied. In this study, the effects and molecular targets of methanol extract of SR (SRme) in hyperlipidemic mice were investigated.
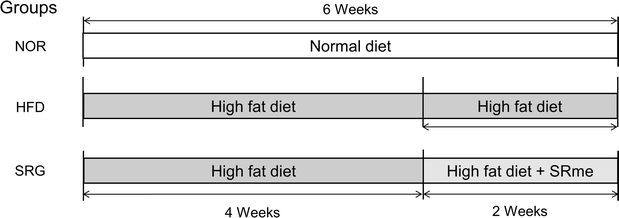
Methods: High-fat diet was fed to mice to induce hyperlipidemia, and measurement of blood cholesterol and triglycerides were conducted to evaluate the effect of SRme on hyperlipidemic mice, and gene expression in mice liver was analyzed to identify key molecules which could be potential targets for developing anti-hyperlipidemic herbal medicines.
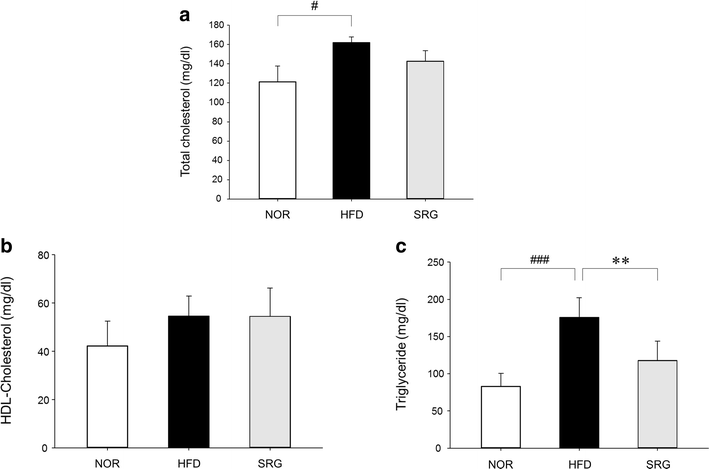
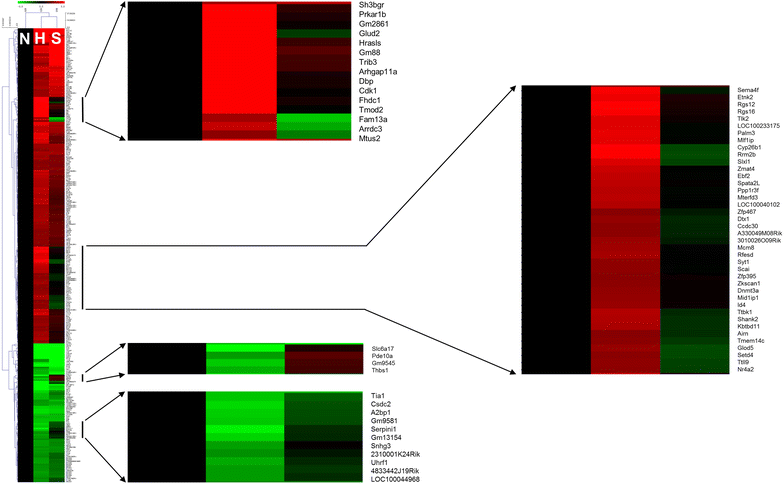
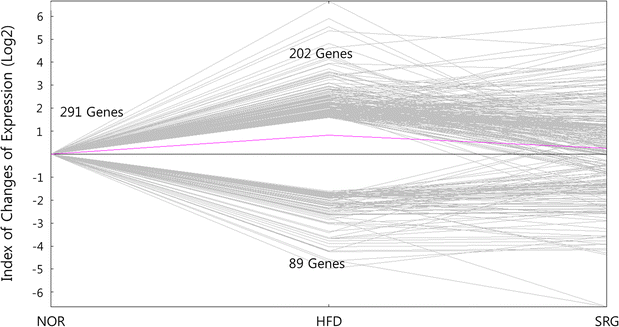
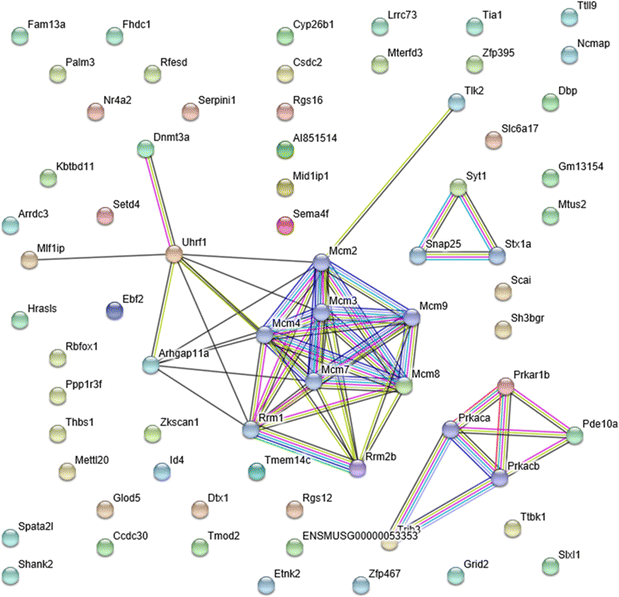
Results: There was no significant effect on the body weight gain of hyperlipidemic mice, but the triglyceride content in blood was significantly reduced by the administration of SRme to hyperlipidemic mice. Proteins such as minichromosome maintenance (Mcm) family which play a key role in DNA replication were identified as molecular targets in the amelioration of hyperlipidemia.
Conclusions: SRme ameliorated hyperlipidemia in high-fat diet fed mice by inhibiting increase of blood serum level of triglycerides. And several proteins such as Mcm proteins were deduced to be molecular targets in treating hyperlipidemia.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Hyperlipidemia; Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix.
Figures


References
-
- Bao CD, Sun B, Lan L, Qiao H, Zhang DF, Liu XY, Wang J, Zhao YS. Interaction between family history of diabetes and hyperlipidemia on risk of diabetes in population with normotension in Harbin: a cross-sectional study. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2017;38(5):611–614. - PubMed
-
- Danese MD, Gleeson M, Griffiths RI, Catterick D, Kutikova L. Methods for estimating costs in patients with hyperlipidemia experiencing their first cardiovascular event in the United Kingdom. J Med Econ. 2017 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

