Factors determining dry deposition of total mercury and organic carbon in house dust of residents of the Tri-city and the surrounding area (Baltic Sea coast)
- PMID: 29046736
- PMCID: PMC5624982
- DOI: 10.1007/s11869-017-0471-2
Factors determining dry deposition of total mercury and organic carbon in house dust of residents of the Tri-city and the surrounding area (Baltic Sea coast)
Abstract
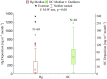
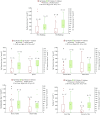
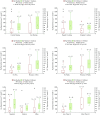
The purpose of this study was to find out what factors determine the deposition levels of mercury and organic carbon in household dust in the Tri-city region (southern Baltic Sea coast). Analyses were performed on samples collected over the period of 2 years, from 2013 to 2015, always in the heating season. The deposition of organic carbon was between 4and 210 mg m-2 month-1, while mercury deposition ranged from 4 to 1336 ng m-2 month-1. Deposition of mercury in household dust during the heating season was three times lower and deposition of organic carbon one and a half times lower than outdoor deposition obtained in the Baltic Sea region by other researchers. In the non-heating period, deposition of mercury in household dust was similar to outdoor deposition while deposition of OC was one and a half times higher. Both of the analyzed dust components reached higher deposition in rural areas than in cities, and both mercury and organic carbon were found to have higher deposition in single-family houses than in buildings housing several families. The increased level of OC was conditioned by the vicinity of the building to a road or street with a high level of traffic, and dust collected on the ground floor had higher Hg depositions. The presence of plants and pets, as well as smoking more than ten cigarettes per day, resulted in higher depositions of both the compounds present in household dust within the Tri-city region.
Keywords: Carbon; Deposition; Household dust; Mercury; Poland; Tri-city.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mercury bonds with carbon (OC and EC) in small aerosols (PM1) in the urbanized coastal zone of the Gulf of Gdansk (southern Baltic).Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Aug 15;157:350-357. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.097. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 29631090
-
Watershed characteristics and climate factors effect on the temporal variability of mercury in the southern Baltic Sea rivers.J Environ Sci (China). 2018 Jun;68:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.11.030. Epub 2018 Mar 19. J Environ Sci (China). 2018. PMID: 29908745
-
Binding of mercury in soils and attic dust in the Idrija mercury mine area (Slovenia).Sci Total Environ. 2006 Oct 1;369(1-3):150-62. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.05.006. Epub 2006 Jun 9. Sci Total Environ. 2006. PMID: 16764912
-
Factors influencing variability of mercury input to the southern Baltic Sea.Mar Pollut Bull. 2014 Sep 15;86(1-2):283-290. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Mar Pollut Bull. 2014. PMID: 25066454
-
Mercury in the atmospheric and coastal environments of Mexico.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2013;226:65-99. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-6898-1_3. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23625130 Review.
Cited by
-
Gaseous Pollutants and Particulate Matter (PM) in Ambient Air and the Number of New Cases of Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Feb 11;2020:1648264. doi: 10.1155/2020/1648264. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32099842 Free PMC article.
-
Origins and discrimination between local and regional atmospheric pollution in Haiphong (Vietnam), based on metal(loid) concentrations and lead isotopic ratios in PM10.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Sep;25(26):26653-26668. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2722-7. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30003484
-
Lesser-Known Cyanotoxins: A Comprehensive Review of Their Health and Environmental Impacts.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Dec 19;16(12):551. doi: 10.3390/toxins16120551. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728809 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bełdowska M, Saniewska D, Falkowska L, Lewandowska A. Mercury in particulate matter over Polish zone of the southern Baltic Sea. Atmos Environ. 2012;46:397–404. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.09.046. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
