Complete genome sequence of Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7
- PMID: 29046741
- PMCID: PMC5637354
- DOI: 10.1186/s40793-017-0271-1
Complete genome sequence of Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7
Abstract
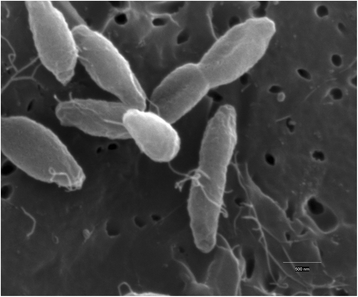
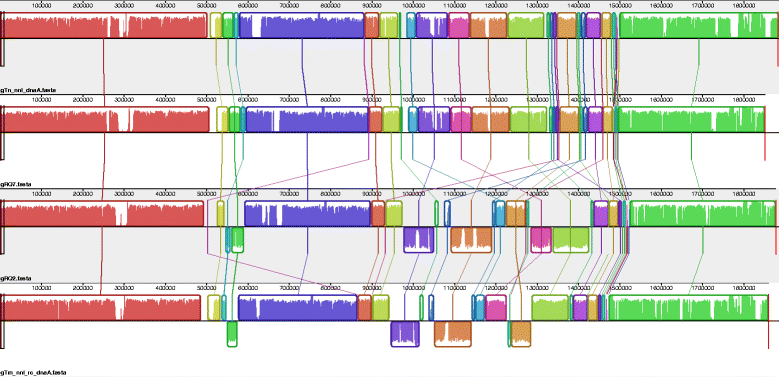
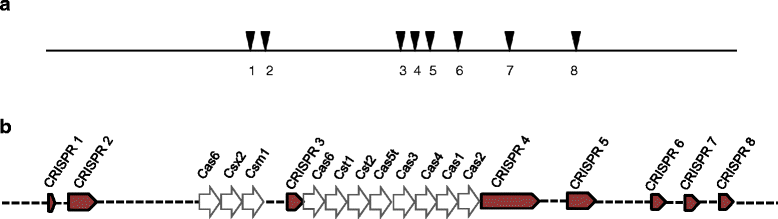
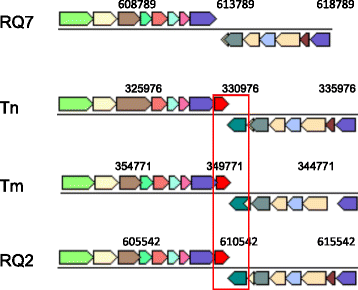
Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7 is a member of the family Thermotogaceae in the order Thermotogales. It is a Gram negative, hyperthermophilic, and strictly anaerobic bacterium. It grows on diverse simple and complex carbohydrates and can use protons as the final electron acceptor. Its complete genome is composed of a chromosome of 1,851,618 bp and a plasmid of 846 bp. The chromosome contains 1906 putative genes, including 1853 protein coding genes and 53 RNA genes. The genetic features pertaining to various lateral gene transfer mechanisms are analyzed. The genome carries a complete set of putative competence genes, 8 loci of CRISPRs, and a deletion of a well-conserved Type II R-M system.
Keywords: CP007633; CRISPR; Natural competence; Restriction-modification system; T. sp. strain RQ7; Thermotoga; TneDI.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Construction and Validation of a Genome-Scale Metabolic Network of Thermotoga sp. Strain RQ7.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;193(3):896-911. doi: 10.1007/s12010-020-03470-z. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33200269
-
Occurrence of Capnophilic Lactic Fermentation in the Hyperthermophilic Anaerobic Bacterium Thermotoga sp. Strain RQ7.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12049. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912049. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233345 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a pyrE-based selective system for Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7.Extremophiles. 2017 Mar;21(2):297-306. doi: 10.1007/s00792-016-0902-2. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Extremophiles. 2017. PMID: 27928679
-
Natural transformation of Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7.BMC Biotechnol. 2014 May 10;14:39. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-14-39. BMC Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24884561 Free PMC article.
-
A cryptic miniplasmid from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7.J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(9):2759-62. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2759-2762.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 8169230 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Construction and Validation of a Genome-Scale Metabolic Network of Thermotoga sp. Strain RQ7.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;193(3):896-911. doi: 10.1007/s12010-020-03470-z. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33200269
-
Fervidobacterium pennivorans subsp. keratinolyticus subsp. nov., a Novel Feather-Degrading Anaerobic Thermophile.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 21;11(1):22. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010022. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677314 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Capnophilic Lactic Fermentation in the Hyperthermophilic Anaerobic Bacterium Thermotoga sp. Strain RQ7.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12049. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912049. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233345 Free PMC article.
-
Adapted laboratory evolution of Thermotoga sp. strain RQ7 under carbon starvation.BMC Res Notes. 2022 Mar 10;15(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13104-022-05982-9. BMC Res Notes. 2022. PMID: 35272671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huber R, Langworthy TA, Konig H, Thomm M, Woese CR, Sleytr UB, Stetter KO. Thermotoga maritima sp. nov. represents a new genus of unique extremely thermophilic eubacteria growing up to 90 degrees C. Arch Microbiol. 1986;144(4):324–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00409880. - DOI
-
- Schroder C, Selig M, Schonheit P. Glucose Fermentation to Acetate, CO2 and H2 in the Anaerobic Hyperthermophilic Eubacterium Thermotoga Maritima: Involvement of the Embden-Meyerhof Pathway. Arch Microbiol. 1994;161(6):460–470.
-
- Zhaxybayeva O, Swithers KS, Lapierre P, Fournier GP, Bickhart DM, DeBoy RT, Nelson KE, Nesbo CL, Doolittle WF, Gogarten JP, et al. On the chimeric nature, thermophilic origin, and phylogenetic placement of the Thermotogales. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(14):5865–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901260106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

