Monitoring of recurrent and superior laryngeal nerve function using an Airwayscope™ during thyroid surgery
- PMID: 29046798
- PMCID: PMC5639316
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2017.1385
Monitoring of recurrent and superior laryngeal nerve function using an Airwayscope™ during thyroid surgery
Abstract
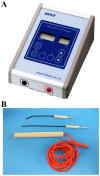
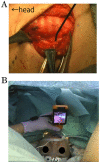
In thyroid surgery, intraoperative identification and preservation of the recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) and superior laryngeal nerve external branch (SLNEB) are crucial. Several reports have proposed that electromyography (EMG) monitoring is an acceptable adjunct for identification and preservation of the RLN. However, a limited number of hospitals have access to an EMG monitoring system. Therefore, the development of another viable monitoring method is required. The aim of the present study was to design a new RLN and SLNEB monitoring method combining an Airwayscope™ (AWS) and a facial nerve stimulator. The facial nerve-stimulating electrode stimulates the RLN or SLNEB, so that the movement of the vocal cord may be observed with an AWS. This monitoring method was performed on 10 patients with a thyroid tumor. In all the cases, RLN and SLNEB were identified and vocal cord function was preserved. All the patients exhibited normal vocal cord function following surgery. Thus, the new RLN and SLNEB monitoring method using an AWS and a facial nerve stimulator is useful in thyroid surgery, and this method may be used as a reliable and available alternative to EMG monitoring to ensure the normal function of the vocal cord.
Keywords: Airwayscope™; laryngeal nerve; nerve monitoring; recurrent nerve; thyroid surgery.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recurrent laryngeal nerve identification and assessment during thyroid surgery: laryngeal palpation.World J Surg. 2004 Aug;28(8):755-60. doi: 10.1007/s00268-004-7348-x. Epub 2004 Aug 3. World J Surg. 2004. PMID: 15457354
-
Superior laryngeal nerve quantitative intraoperative monitoring is possible in all thyroid surgeries.Laryngoscope. 2014 Apr;124(4):1035-41. doi: 10.1002/lary.24446. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Laryngoscope. 2014. PMID: 24115215
-
A Review of Methods for the Preservation of Laryngeal Nerves During Thyroidectomy.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018 Jun 18;52(2):79-91. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2018.37928. eCollection 2018. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2018. PMID: 32595378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The electrophysiology of thyroid surgery: electrophysiologic and muscular responses with stimulation of the vagus nerve, recurrent laryngeal nerve, and external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve.Laryngoscope. 2017 Mar;127(3):764-771. doi: 10.1002/lary.26147. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Laryngoscope. 2017. PMID: 27374859
-
External branch of the superior laryngeal nerve monitoring during thyroid and parathyroid surgery: International Neural Monitoring Study Group standards guideline statement.Laryngoscope. 2013 Sep;123 Suppl 4:S1-14. doi: 10.1002/lary.24301. Laryngoscope. 2013. PMID: 23832799 Review.
References
-
- Tomoda C, Hirokawa Y, Uruno T, Takamura Y, Ito Y, Miya A, Kobayashi K, Matsuzuka F, Kuma K, Miyauchi A. Sensitivity and specificity of intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve stimulation test for predicting vocal cord palsy after thyroid surgery. World J Surg. 2006;30:1230–1233. doi: 10.1007/s00268-005-0351-z. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
