Development of a fully automated chemiluminescence immunoassay for urine monomeric laminin-γ2 as a promising diagnostic tool of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- PMID: 29046806
- PMCID: PMC5640956
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-017-0109-4
Development of a fully automated chemiluminescence immunoassay for urine monomeric laminin-γ2 as a promising diagnostic tool of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
Abstract
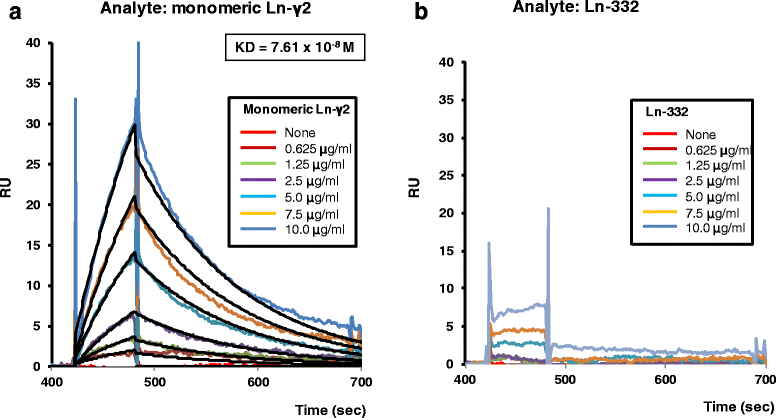
Background: Monomeric laminin-γ2 in urine is a potential biomarker for bladder cancer. However, the current detection system uses an antibody that cannot discriminate between monomeric laminin-γ2 and the heterotrimeric γ2 chain of laminin-332, which may cause false-positive reactions. The present study aimed to develop a fully automated chemiluminescence immunoassay system using a specific monoclonal antibody against monomeric laminin-γ2.
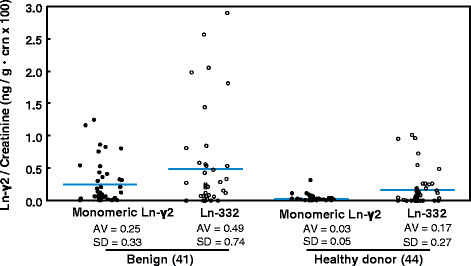
Methods: In total, 237 urine specimens (84 from patients with bladder cancer, 48 from patients with benign urological disease, and 105 from healthy donors) were collected, and monomeric laminin-γ2 values in the urine were measured using a fully automated chemiluminescence immunoassay.
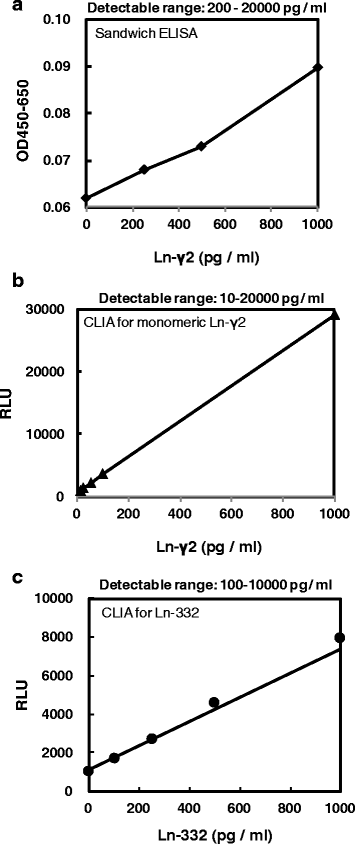
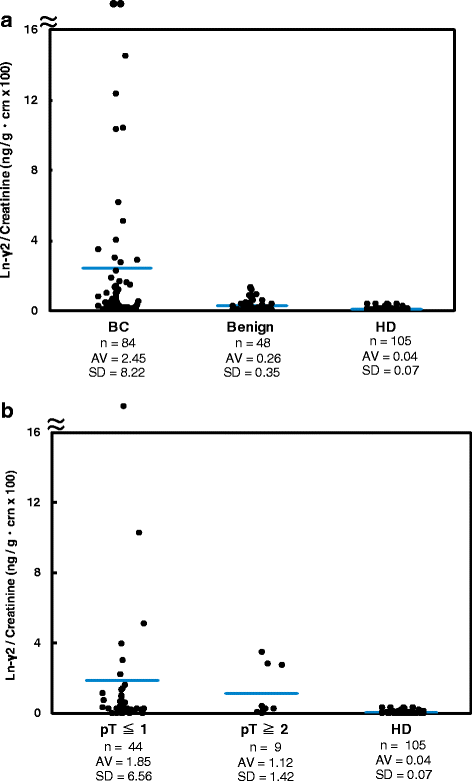
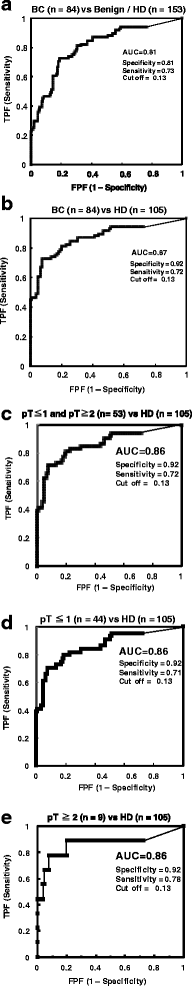
Results: The results revealed that laminin-γ2 values in patients with benign urological disease were comparable to those of healthy donors and that the chemiluminescence immunoassay's lower limit of detection was 10 pg/mL (approximately 20-fold better than the sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay's limit of 200 pg/mL). Moreover, the chemiluminescence immunoassay demonstrated that patients with bladder cancer, including non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (≤pT1), had higher laminin-γ2 values than patients with benign urological disease or healthy donors.
Conclusions: These results suggest that urine monomeric laminin-γ2 may be a promising biomarker to diagnose cases of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer using a fully automated chemiluminescence immunoassay system.
Keywords: Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA); Monomeric laminin-γ2; Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC); Urine biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All patients and HDs provided written informed consent, and the study protocol was approved by our institutional review boards (Kochi Medical School Hospital: 24–139; Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyo: 20–52-0123; Kanagawa Cancer Center: Res-36).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Research funding from Abbott Laboratories (North Chicago, IL) was received by NK.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unique Biological Activity and Potential Role of Monomeric Laminin-γ2 as a Novel Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 8;20(1):226. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010226. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30626121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical evaluation of urine laminin-γ2 monomer as a potent biomarker for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(3):2453-2462. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5087. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35924681 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary laminin-γ2 is a novel biomarker of non-muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2015 Dec;106(12):1730-7. doi: 10.1111/cas.12832. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26450632 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of laminin gamma2 chain monomer enhances invasive growth of human carcinoma cells in vivo.Int J Cancer. 2010 Nov 1;127(9):2031-41. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25231. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20143393
-
Urinary Cell-Free DNA in Bladder Cancer Detection.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Feb 14;11(2):306. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11020306. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review: Detection and quantification of proteins in human urine.Talanta. 2021 Feb 1;223(Pt 1):121718. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121718. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 33303164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unique Biological Activity and Potential Role of Monomeric Laminin-γ2 as a Novel Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 8;20(1):226. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010226. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30626121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging Biosensors for Determination of Fibronectin, Laminin-5, and Type IV Collagen in Plasma, Urine, and Tissue of Renal Cell Carcinoma.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;24(19):6371. doi: 10.3390/s24196371. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409411 Free PMC article.
-
EphA2 Proteolytic Fragment as a Sensitive Diagnostic Biomarker for Very Early-stage Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma.Cancer Res Commun. 2023 Sep 15;3(9):1862-1874. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0087. Cancer Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37712876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watanabe JNA, Ogawa O. Bladder cancer practice guideline. IGAKUTOSHO. 2009;1:1.
-
- Badalament RA, Hermansen DK, Kimmel M, Gay H, Herr HW, Fair WR, Whitmore WF, Jr, Melamed MR. The sensitivity of bladder wash flow cytometry, bladder wash cytology, and voided cytology in the detection of bladder carcinoma. Cancer. 1987;60:1423–1427. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19871001)60:7<1423::AID-CNCR2820600702>3.0.CO;2-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

