Development of an elution device for ViroCap virus filters
- PMID: 29046968
- PMCID: PMC5648745
- DOI: 10.1007/s10661-017-6258-y
Development of an elution device for ViroCap virus filters
Abstract
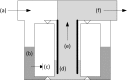
Environmental surveillance of waterborne pathogens is vital for monitoring the spread of diseases, and electropositive filters are frequently used for sampling wastewater and wastewater-impacted surface water. Viruses adsorbed to electropositive filters require elution prior to detection or quantification. Elution is typically facilitated by a peristaltic pump, although this requires a significant startup cost and does not include biosafety or cross-contamination considerations. These factors may pose a barrier for low-resource laboratories that aim to conduct environmental surveillance of viruses. The objective of this study was to develop a biologically enclosed, manually powered, low-cost device for effectively eluting from electropositive ViroCap™ virus filters. The elution device described here utilizes a non-electric bilge pump, instead of an electric peristaltic pump or a positive pressure vessel. The elution device also fully encloses liquids and aerosols that could contain biological organisms, thereby increasing biosafety. Moreover, all elution device components that are used in the biosafety cabinet are autoclavable, reducing cross-contamination potential. This device reduces costs of materials while maintaining convenience in terms of size and weight. With this new device, there is little sample volume loss due to device inefficiency, similar virus yields were demonstrated during seeded studies with poliovirus type 1, and the time to elute filters is similar to that required with the peristaltic pump. The efforts described here resulted in a novel, low-cost, manually powered elution device that can facilitate environmental surveillance of pathogens through effective virus recovery from ViroCap filters while maintaining the potential for adaptability to other cartridge filters.
Keywords: Electropositive filter; Environmental surveillance; Poliovirus; ViroCap filter; Virus elution; Wastewater.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of Preservative Agents and Antibiotics for Increased Poliovirus Survival on Positively Charged Filters.Food Environ Virol. 2017 Dec;9(4):383-394. doi: 10.1007/s12560-017-9306-4. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Food Environ Virol. 2017. PMID: 28616833 Free PMC article.
-
Poliovirus concentration from tap water with electropositive adsorbent filters.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):201-10. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.201-210.1980. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980. PMID: 6258472 Free PMC article.
-
New electropositive filter for concentrating enteroviruses and noroviruses from large volumes of water.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Apr;75(8):2393-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00922-08. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19218410 Free PMC article.
-
Concentration and recovery of viruses from water: a comprehensive review.Food Environ Virol. 2012 Jun;4(2):41-67. doi: 10.1007/s12560-012-9080-2. Epub 2012 May 31. Food Environ Virol. 2012. PMID: 23412811 Review.
-
Cellulose-based virus-retentive filters: a review.Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2017;16(3):455-489. doi: 10.1007/s11157-017-9434-1. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 32214924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of the bag-mediated filtration system for environmental surveillance of poliovirus in Nairobi, Kenya.J Appl Microbiol. 2021 Mar;130(3):971-981. doi: 10.1111/jam.14807. Epub 2020 Aug 14. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32743931 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Sampling and Concentration Methods for Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Detection from Wastewater.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2023 Feb 6;108(3):482-491. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.22-0427. Print 2023 Mar 1. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2023. PMID: 36746655 Free PMC article.
-
Field Performance of Two Methods for Detection of Poliovirus in Wastewater Samples, Mexico 2016-2017.Food Environ Virol. 2019 Dec;11(4):364-373. doi: 10.1007/s12560-019-09399-9. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Food Environ Virol. 2019. PMID: 31571037 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Wastewater Pooled Surveillance of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from Congregate Living Settings.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Jun 11;87(13):e0043321. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00433-21. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33858836 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Most Commonly Used Methods for Sample Collection in Environmental Surveillance of Poliovirus.Clin Infect Dis. 2018 Oct 30;67(suppl_1):S90-S97. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy638. Clin Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30376094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams MH. Bacteriophages. New York: Interscience Publishers; 1959.
-
- Battistone A, Buttinelli G, Fiore S, Amato C, Bonomo P, Patti AM, et al. Sporadic isolation of sabin-like polioviruses and high-level detection of non-polio enteroviruses during sewage surveillance in seven Italian cities, after several years of inactivated poliovirus vaccination. [Article] Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2014;80(15):4491–4501. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00108-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

