Heparin-binding protein (HBP) improves prediction of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- PMID: 29047023
- PMCID: PMC5647316
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-017-0330-1
Heparin-binding protein (HBP) improves prediction of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
Abstract
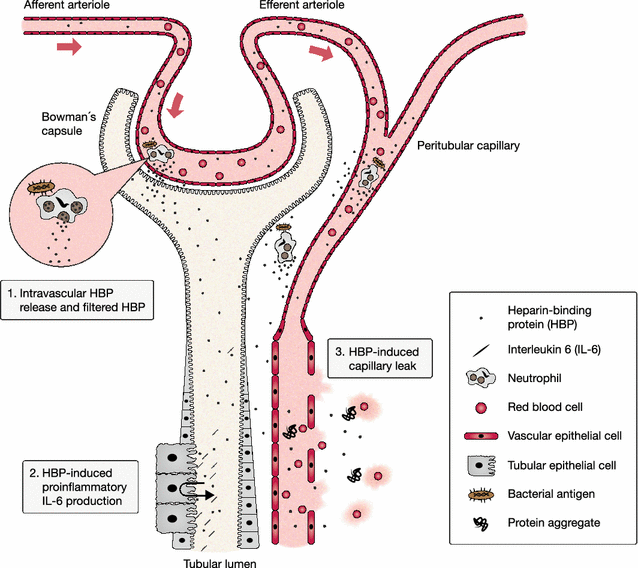
Background: Sepsis-related acute kidney injury (AKI) accounts for major morbidity and mortality among the critically ill. Heparin-binding protein (HBP) is a promising biomarker in predicting development and prognosis of severe sepsis and septic shock that has recently been proposed to be involved in the pathophysiology of AKI. The objective of this study was to investigate the added predictive value of measuring plasma HBP on admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) regarding the development of septic AKI.
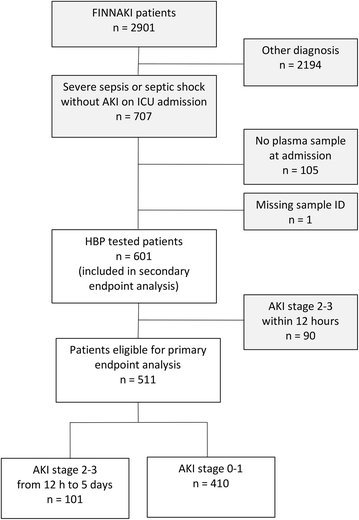
Methods: We included 601 patients with severe sepsis or septic shock from the prospective, observational FINNAKI study conducted in seventeen Finnish ICUs during a 5-month period (1 September 2011-1 February 2012). The main outcome measure was the development of KDIGO AKI stages 2-3 from 12 h after admission up to 5 days. Statistical analysis for the primary endpoint included construction of a clinical risk model, area under the receiver operating curve (ROC area), category-free net reclassification index (cfNRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI).
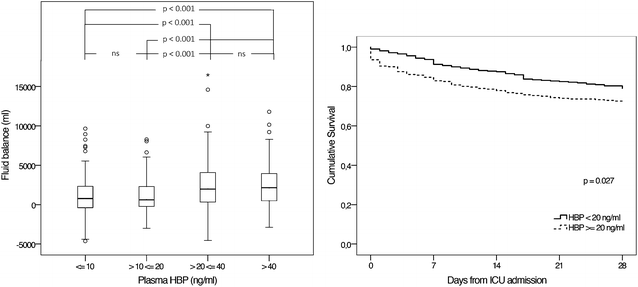
Results: Out of 511 eligible patients, 101 (20%) reached the primary endpoint. The addition of plasma HBP to a clinical risk model significantly increased ROC area (0.82 vs. 0.78, p = 0.03) and risk classification scores: cfNRI 62.0% (95% CI 40.5-82.4%) and IDI 0.053 (95% CI 0.029-0.075).
Conclusions: Plasma HBP adds predictive value to known clinical risk factors in septic AKI. Further studies are warranted to compare the predictive performance of plasma HBP to other novel AKI biomarkers.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Biomarker; Heparin-binding protein; Risk model; Sepsis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heparin-Binding Protein (HBP): A Causative Marker and Potential Target for Heparin Treatment of Human Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury.Shock. 2017 Sep;48(3):313-320. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000862. Shock. 2017. PMID: 28319494 Clinical Trial.
-
Hepcidin, in contrast to heparin binding protein, does not portend acute kidney injury in patients with community acquired septic shock.PLoS One. 2024 May 2;19(5):e0299257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299257. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38696394 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of SOFA score and biomarkers gives a better prediction of septic AKI and in-hospital mortality in critically ill surgical patients: a pilot study.World J Emerg Surg. 2018 Sep 10;13:41. doi: 10.1186/s13017-018-0202-5. eCollection 2018. World J Emerg Surg. 2018. PMID: 30214469 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated plasma levels of heparin-binding protein in intensive care unit patients with severe sepsis and septic shock.Crit Care. 2012 May 21;16(3):R90. doi: 10.1186/cc11353. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22613179 Free PMC article.
-
A promising marker in early diagnosis of septic acute kidney injury of critically ill patients: urine insulin like growth factor binding protein-7.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2016 Sep;76(5):402-10. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2016.1187765. Epub 2016 May 31. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27240440
Cited by
-
Renal clearance of heparin-binding protein and elimination during renal replacement therapy: Studies in ICU patients and healthy volunteers.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 29;14(8):e0221813. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221813. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31465432 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated measures of Heparin-binding protein (HBP) and procalcitonin during septic shock: biomarker kinetics and association with cardiovascular organ dysfunction.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020 Sep 10;8(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s40635-020-00338-8. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020. PMID: 32910266 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of the Thrombotic Microangiopathy Score as a Promising Prognostic Marker of Septic Shock for Patients in the Emergency Department.J Clin Med. 2019 Jun 6;8(6):808. doi: 10.3390/jcm8060808. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31174267 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding protein in sepsis: player! predictor! positioning?Ann Intensive Care. 2019 Jun 20;9(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13613-019-0546-3. Ann Intensive Care. 2019. PMID: 31222522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Combined detection of procalcitonin, heparin-binding protein, and interleukin-6 is a promising assay to diagnose and predict acute pancreatitis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Aug;35(8):e23869. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23869. Epub 2021 Jun 21. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34151489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Group. KDIGOKAKIW KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2(Suppl.):1–138.
-
- Murray PT, Mehta RL, Shaw A, Ronco C, Endre Z, Kellum JA, et al. Potential use of biomarkers in acute kidney injury: report and summary of recommendations from the 10th acute dialysis quality initiative consensus conference. Kidney Int. 2014;85(3):513–521. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.374. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

