Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system for cancer treatment: discovering novel inhibitors from nature and drug repurposing
- PMID: 29047025
- PMCID: PMC5722705
- DOI: 10.1007/s10555-017-9705-x
Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system for cancer treatment: discovering novel inhibitors from nature and drug repurposing
Abstract
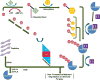
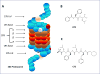
In the past 15 years, the proteasome has been validated as an anti-cancer drug target and 20S proteasome inhibitors (such as bortezomib and carfilzomib) have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of multiple myeloma and some other liquid tumors. However, there are shortcomings of clinical proteasome inhibitors, including severe toxicity, drug resistance, and no effect in solid tumors. At the same time, extensive research has been conducted in the areas of natural compounds and old drug repositioning towards the goal of discovering effective, economical, low toxicity proteasome-inhibitory anti-cancer drugs. A variety of dietary polyphenols, medicinal molecules, metallic complexes, and metal-binding compounds have been found to be able to selectively inhibit tumor cellular proteasomes and induce apoptotic cell death in vitro and in vivo, supporting the clinical success of specific 20S proteasome inhibitors bortezomib and carfilzomib. Therefore, the discovery of natural proteasome inhibitors and researching old drugs with proteasome-inhibitory properties may provide an alternative strategy for improving the current status of cancer treatment and even prevention.
Keywords: 26S proteasome; Cancer therapy and prevention; Drug repurposing; Metal complexes; Natural compounds; Proteasome inhibitor; Protein degradation; Tea polyphenols.
Figures

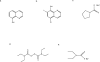
References
-
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1994;79(1):13–21. - PubMed
-
- Hochstrasser M. Ubiquitin, proteasomes, and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7(2):215–223. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg AL, Akopian TN, Kisselev AF, Lee DH, Rohrwild M. New insights into the mechanisms and importance of the proteasome in intracellular protein degradation. Biol Chem. 1997;378(3–4):131–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

