De novo implantation vs. upgrade cardiac resynchronization therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29047028
- PMCID: PMC5756552
- DOI: 10.1007/s10741-017-9652-1
De novo implantation vs. upgrade cardiac resynchronization therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
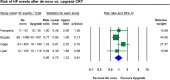
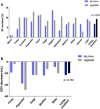
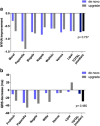
Patients with conventional pacemakers or implanted defibrillators are often considered for cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Our aim was to summarize the available evidences regarding the clinical benefits of upgrade procedures. A systematic literature search was performed from studies published between 2006 and 2017 in order to compare the outcome of CRT upgrade vs. de novo implantations. Outcome data on all-cause mortality, heart failure events, New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class, QRS narrowing and echocardiographic parameters were analysed. A total of 16 reports were analysed comprising 489,568 CRT recipients, of whom 468,205 patients underwent de novo and 21,363 upgrade procedures. All-cause mortality was similar after CRT upgrade compared to de novo implantations (RR 1.19, 95% CI 0.88-1.60, p = 0.27). The risk of heart failure was also similar in both groups (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.70-1.32, p = 0.81). There was no significant difference in clinical response after CRT upgrade compared to de novo implantations in terms of improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction (ΔEF de novo - 6.85% vs. upgrade - 9.35%; p = 0.235), NYHA class (ΔNYHA de novo - 0.74 vs. upgrade - 0.70; p = 0.737) and QRS narrowing (ΔQRS de novo - 9.6 ms vs. upgrade - 29.5 ms; p = 0.485). Our systematic review and meta-analysis of currently available studies reports that CRT upgrade is associated with similar risk for all-cause mortality compared to de novo resynchronization therapy. Benefits on reverse remodelling and functional capacity improved similarly in both groups suggesting that CRT upgrade may be safely and effectively offered in routine practice.
Clinical trial registration: Prospero Database-CRD42016043747.
Keywords: CRT upgrade; Cardiac resynchronization therapy; De novo CRT; Heart failure; Meta-analyses; Mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Mate Vamos reports lecture fees from Bayer, Pfizer and Spectranetics and support attending scientific meetings from Bayer, Boston Scientific, Pfizer and SJM, outside the submitted work. Endre Zima reports consulting fees and honoraria from Bayer, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Innomed, Medtronic and St. Jude Medical for lectures, training and participation in clinical trials. Laszlo Geller reports consulting fees/honoraria from Biotronik, Medtronic, St. Jude Medical and Johnson & Johnson. Gabor Z. Duray served as a member of the steering committee of the Micra Study and reports research grants from Boston Scientific, Biotronik and Medtronic and speakers bureau/consulting fees from Biotronik, Medtronic, St. Jude Medical, Bayer and Boehringer Ingelheim. Bela Merkely reports consulting/lecture fees from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, St. Jude Medical and Terumo.
Annamaria Kosztin, Daniel Aradi, Attila Kovacs, Richard Schwertner, Valentina Kutyifa and Klaudia Vivien Nagy have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS, Klein H, Brown MW, Daubert JP, Estes NA, 3rd, Foster E, Greenberg H, Higgins SL, Pfeffer MA, Solomon SD, Wilber D, Zareba W. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for the prevention of heart-failure events. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(14):1329–1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0906431. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sweeney MO, Hellkamp AS, Ellenbogen KA, Greenspon AJ, Freedman RA, Lee KL, Lamas GA. Adverse effect of ventricular pacing on heart failure and atrial fibrillation among patients with normal baseline QRS duration in a clinical trial of pacemaker therapy for sinus node dysfunction. Circulation. 2003;107(23):2932–2937. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000072769.17295.B1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilkoff BL, Cook JR, Epstein AE, Greene HL, Hallstrom AP, Hsia H, Kutalek SP, Sharma A. Dual-chamber pacing or ventricular backup pacing in patients with an implantable defibrillator: the Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator (DAVID) Trial. JAMA. 2002;288(24):3115–3123. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.24.3115. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Birnie DH, Ha A, Higginson L, Sidhu K, Green M, Philippon F, Thibault B, Wells G, Tang A. Impact of QRS morphology and duration on outcomes after cardiac resynchronization therapy: results from the Resynchronization-Defibrillation for Ambulatory Heart Failure Trial (RAFT) Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6(6):1190–1198. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000380. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zareba W, Klein H, Cygankiewicz I, Hall WJ, McNitt S, Brown M, Cannom D, Daubert JP, Eldar M, Gold MR, Goldberger JJ, Goldenberg I, Lichstein E, Pitschner H, Rashtian M, Solomon S, Viskin S, Wang P, Moss AJ. Effectiveness of cardiac resynchronization therapy by QRS morphology in the Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial-Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT-CRT) Circulation. 2011;123(10):1061–1072. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.960898. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

