The presence of Philadelphia chromosome does not confer poor prognosis in adult pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era - a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database analysis
- PMID: 29047122
- PMCID: PMC7546179
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.14953
The presence of Philadelphia chromosome does not confer poor prognosis in adult pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era - a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database analysis
Abstract
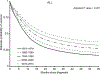
The BCR-ABL1 fusion gene is caused by a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, resulting in an abnormal chromosome 22 (Philadelphia chromosome; Ph). Prior to the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), the presence of BCR-ABL1 conferred a poor prognosis in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL). We compared the survival of Ph+ and Ph-ALL during the period when TKIs were universally available in the US for Ph+ALL, using a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database analysis. A total of 2694 patients with pre-B ALL (206 Ph+ALL; 2488 Ph-ALL) aged ≥18 years, who were diagnosed between 2010 and 2014, were identified in SEER registries. The median overall survival (OS) was 32 months in Ph+ALL (95% confidence interval [CI] 18 months-not reached) and 27 months (95% CI 24-30 months) in Ph-ALL (Log-rank test P-value 0·34). Older age was associated with worse prognosis in both Ph+ALL and Ph-ALL. Age-adjusted OS was inferior in Hispanics and African-Americans compared to non-Hispanic whites. Survival of pre-B ALL shows continued improvement with time. Philadelphia chromosome status does not confer poor prognosis in pre-B ALL in the TKI era: prognostic factors in pre-B ALL should be re-evaluated in the light of this finding.
Keywords: SEER; acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; philadelphia chromosome; survival; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


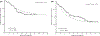
References
-
- Arico M, Valsecchi MG, Camitta B, Schrappe M, Chessells J, Baruchel A, Gaynon P, Silverman L, Janka-Schaub G, Kamps W, Pui CH & Masera G (2000) Outcome of treatment in children with philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The New England Journal of Medicine, 342, 998–1006. - PubMed
-
- Avivi I & Goldstone AH (2003) Bone marrow transplant in ph+ ALL patients. Bone Marrow Transplantation, 31, 623–632. - PubMed
-
- Bassan R & Hoelzer D (2011) Modern therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of Clinical Oncology: Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 29, 532–543. - PubMed
-
- Burmeister T, Schwartz S, Bartram CR, Gokbuget N, Hoelzer D, Thiel E; GMALL study group. (2008) Patients’ age and BCR-ABL frequency in adult B-precursor ALL: a retrospective analysis from the GMALL study group. Blood, 112, 918–919. - PubMed
-
- Chalandon Y, Thomas X, Hayette S, Cayuela JM, Abbal C, Huguet F, Raffoux E, Leguay T, Rousselot P, Lepretre S, Escoffre-Barbe M, Maury S, Berthon C, Tavernier E, Lambert JF, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Lheritier V, Chevret S, Ifrah N & Dombret H; Group for Research on Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (GRAALL). (2015) Randomized study of reduced-intensity chemotherapy combined with imatinib in adults with ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood, 125, 3711–3719. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

