Tanshinone IIA alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by downregulating TRPM7 and pro-inflammatory factors
- PMID: 29047214
- PMCID: PMC5742685
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13350
Tanshinone IIA alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by downregulating TRPM7 and pro-inflammatory factors
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Tanshinone IIA alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by downregulating TRPM7 and pro-inflammatory factors.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(8):e18313. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18313. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38652091 Free PMC article.
Abstract
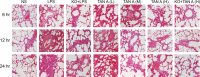
The study aimed to investigate the role of Tanshinone IIA (Tan IIA) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) in its regulation of TRPM7. Wistar male rats were randomly divided into the normal saline (NS), LPS, knockout (KO) + LPS, low-dose Tan IIA (Tan-L), middle-dose Tan IIA (Tan-M), high-dose Tan IIA (Tan-H) and KO + high-dose Tan IIA (KO + Tan-H) groups. The level of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, TRPM7 protein expression, current density-voltage curve and Ca2+ concentration were detected through ELISA, Western blotting, electrophysiological experiment and a calcium-imaging technique, respectively. The rats in the KO + LPS, Tan-L, Tan-M, Tan-H and KO + Tan-H groups all displayed lower levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 than the LPS group. Rats in the KO + Tan-H group exhibited lower levels of NF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 than rats in the Tan-H group. Elevated levels of TRPM7 protein expression in the LPS and Tan groups were detected in comparison with the NS group. However, TRPM7 protein expression in Tan-M and Tan-H groups was notably lower than in that of the LPS group. In comparison with the NS group, the LPS and Tan groups had a greater PIMs cell density and a higher concentration of Ca2+ . Contrary results were observed in the KO + LPS, Tan-H and KO + Tan-H groups. Tan IIA decreases calcium influx in PIMs and inhibits pro-inflammatory factors which provide an alleviatory effect in regards to LPS-induced ALI by suppressing TRPM7 expression.
Keywords: Tanshinone IIA; acute lung injury; interleukin 6; lipopolysaccharide; transient receptor potential melastatin 7; tumour necrosis factor alpha.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures





References
-
- Sebai H, Sani M, Yacoubi MT, et al Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, attenuates lipopolysaccharide‐induced oxidative stress in rat liver. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2010; 73: 1078–83. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Quinn PJ. Lipopolysaccharide: biosynthetic pathway and structure modification. Prog Lipid Res. 2010; 49: 97–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

