Prevalence of multimorbidity in Germany: impact of age and educational level in a cross-sectional study on 19,294 adults
- PMID: 29047341
- PMCID: PMC5648462
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4833-3
Prevalence of multimorbidity in Germany: impact of age and educational level in a cross-sectional study on 19,294 adults
Abstract
Background: Multimorbidity is one of the most important and challenging aspects in public health. Multimorbid people are associated with more hospital admissions, a large number of drug prescriptions and higher risks of mortality. As there is evidence that multimorbidity varies with age and socioeconomic disparity, the main objective aimed at determining age-specific prevalence rates as well as exploring educational differences relating to multimorbidity in Germany.
Methods: This cross-sectional analysis is based on the national telephone health interview survey "German Health Update" (GEDA2012) conducted between March 2012 and March 2013 with nearly 20,000 adults. GEDA2012 provides information on 17 self-reported health conditions along with sociodemographic characteristics. Multimorbidity was defined as the occurrence of two or more chronic conditions in one individual at the same time. Descriptive statistical analysis was used to examine multimorbidity according to age and education, which was defined by the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED 1997).
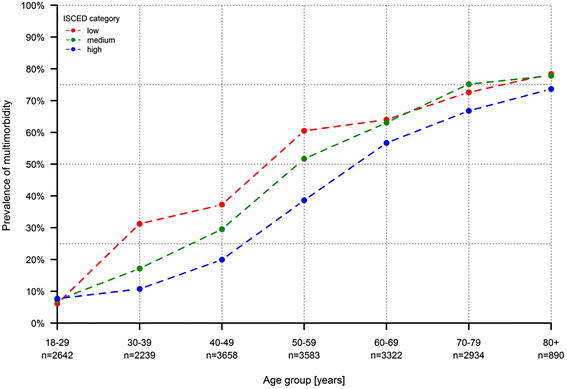
Results: Overall, 39.6% (95% confidence interval (CI) 38.7%-40.6%) of the 19,294 participants were multimorbid and the proportion of adults with multimorbidity increased substantially with age: nearly half (49.2%, 95% CI 46.9%-51.5%) of the adults aged 50-59 years had already two or more chronic health conditions. Prevalence rates of multimorbidity differed considerably between the levels of education. Low-level educated adults aged 40-49 years were more likely to be multimorbid with a prevalence rate of 47.4% (95% CI 44.2%-50.5%) matching those of highly educated men and women aged about ten years older.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that both, age and education are associated with a higher risk of being multimorbid in Germany. Hence, special emphasis in the development of new approaches in national public health and prevention programs on multimorbidity should be given to low-level educated people aged <65 years.
Keywords: Age; Chronic conditions; German health update (GEDA) 2012; Multimorbidity; Socioeconomic status.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable as the analysis is based on secondary data.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- van den Bussche H, Schon G, Kolonko T, Hansen H, Wegscheider K, Glaeske G, Koller D. Patterns of ambulatory medical care utilization in elderly patients with special reference to chronic diseases and multimorbidity--results from a claims data based observational study in Germany. BMC Geriatr. 2011;11:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-11-54. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials