Structural and functional characterization of the divergent Entamoeba Src using Src inhibitor-1
- PMID: 29047404
- PMCID: PMC5648430
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2461-5
Structural and functional characterization of the divergent Entamoeba Src using Src inhibitor-1
Abstract
Background: The abundant number of kinases that Entamoeba histolytica possesses allows us to assume that the regulation of cellular functions by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation processes is very important. However, the kinases responsible for the phosphorylation in Entamoeba spp. vary in the structure of their domains and, therefore, could be responsible for the unusual biological characteristics of this parasite. In higher eukaryotes, Src kinases share conserved structural domains and are very important in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. In both Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba invadens, the major Src kinase homologue of higher eukaryotes lacks SH3 and SH2 domains, but does have KELCH domains; the latter are part of actin cross-linking proteins in higher eukaryotic cells.
Methods: The function of the EhSrc protein kinase of Entamoeba spp. was evaluated using Src inhibitor-1, microscopy assays, Src kinase activity and western blot. In addition, to define the potential inhibitory mechanism of Src-inhibitor-1 for the amoebic EhSrc protein kinase, molecular dynamic simulations using NAnoscale Molecular Dynamics (NAMD2) program and docking studies were performed with MOE software.
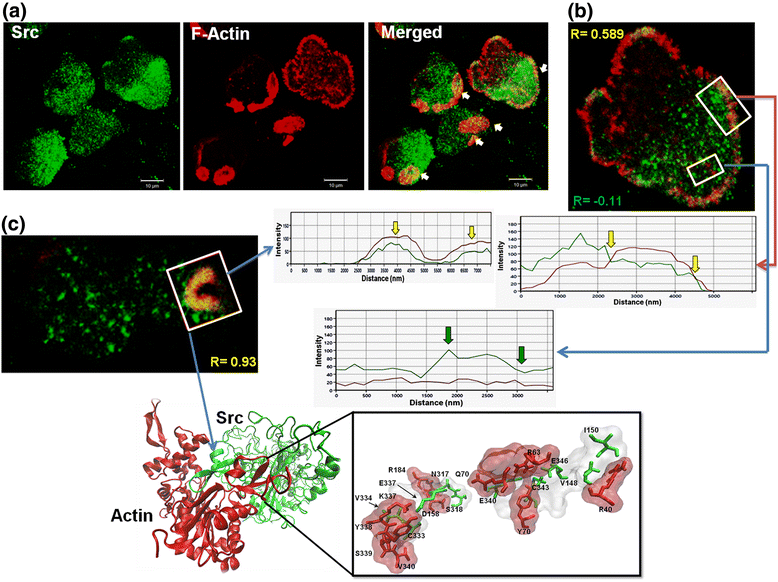
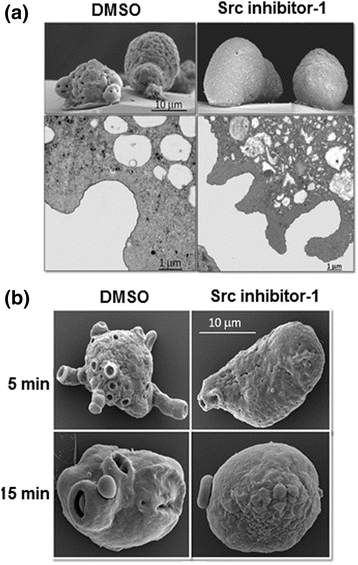
Results: We demonstrate that Src inhibitor-1 is able to prevent the activity of EhSrc protein kinase, most likely by binding to the catalytic domain, which affects cell morphology via the disruption of actin cytoskeleton remodeling and the formation of phagocytic structures without an effect on cell adhesion. Furthermore, in E. invadens, Src inhibitor-1 inhibited the encystment process by blocking RhoA GTPase activity, a small GTPase protein of Rho family.
Conclusions: Even though the EhSrc molecule of Entamoeba is not a typical Src, because its divergent amino acid sequence, it is a critical factor in the biology of this parasite via the regulation of actin cytoskeleton remodeling via RhoA GTPase activation. Based on this, we conclude that EhSrc could become a target molecule for the future design of drugs that can prevent the transmission of the disease.
Keywords: Actin cytoskeleton; EhSrc; Entamoeba spp.; Src inhibitor-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research protocol was approved by CINVESTAV’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (CINVESTAV-IACUC). The procedures were approved by the board of the Animal Production and Experimentation Unit (UPEAL, CINVESTAV). Antibody production was performed with a rabbit provided by UPEAL-CINVESTAV, (Protocol No. 0053–13) following the specifications of the Mexican National Norm (NOM-062-ZOO-1999) that is a version of the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals 2011.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Morphodynamics of the Actin-Rich Cytoskeleton in Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 May 29;8:179. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00179. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29896453 Free PMC article.
-
Src and PI3 K inhibitors affect the virulence factors of Entamoeba histolytica.Parasitology. 2013 Feb;140(2):202-9. doi: 10.1017/S0031182012001540. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Parasitology. 2013. PMID: 23058125
-
Actin, RhoA, and Rab11 participation during encystment in Entamoeba invadens.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:919345. doi: 10.1155/2013/919345. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24175308 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation and function of Rab small GTPases in Entamoeba: annotation of E. invadens Rab and its use for the understanding of Entamoeba biology.Exp Parasitol. 2010 Nov;126(3):337-47. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2010.04.014. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Exp Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20434444 Review.
-
Involvement of the actin cytoskeleton and p21rho-family GTPases in the pathogenesis of the human protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1998 Aug;31(8):1049-58. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1998000800004. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1998. PMID: 9777011 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Phosphatase PP2C Identification in Entamoeba spp.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 16;2021:5746629. doi: 10.1155/2021/5746629. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34697588 Free PMC article.
-
A Review: Natural and Synthetic Compounds Targeting Entamoeba histolytica and Its Biological Membrane.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;12(4):396. doi: 10.3390/membranes12040396. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicological Evaluation of Kaempferol and Linearolactone as Treatments for Amoebic Liver Abscess Development in Mesocricetus auratus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10633. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910633. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408962 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Breast Cancer: The Familiar, the Emerging, and the Uncharted Territories.Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 25;13(9):1306. doi: 10.3390/biom13091306. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haque R, Huston CD, Hughes M, Houpt E. Petri, W A Jr. Amebiasis. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1565–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

