Levosimendan for patients with severely reduced left ventricular systolic function and/or low cardiac output syndrome undergoing cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29047417
- PMCID: PMC5648477
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1849-0
Levosimendan for patients with severely reduced left ventricular systolic function and/or low cardiac output syndrome undergoing cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have shown beneficial effects of levosimendan in high-risk patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Two large randomized controlled trials (RCTs), however, showed no advantages of levosimendan.
Methods: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis (MEDLINE and Embase from inception until March 30, 2017), investigating whether levosimendan offers advantages compared with placebo in high-risk cardiac surgery patients, as defined by preoperative left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤ 35% and/or low cardiac output syndrome (LCOS). The primary outcomes were mortality at longest follow-up and need for postoperative renal replacement therapy (RRT). Secondary postoperative outcomes investigated included myocardial injury, supraventricular arrhythmias, development of LCOS, acute kidney injury (AKI), duration of mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit and hospital lengths of stay, and incidence of hypotension during drug infusion.
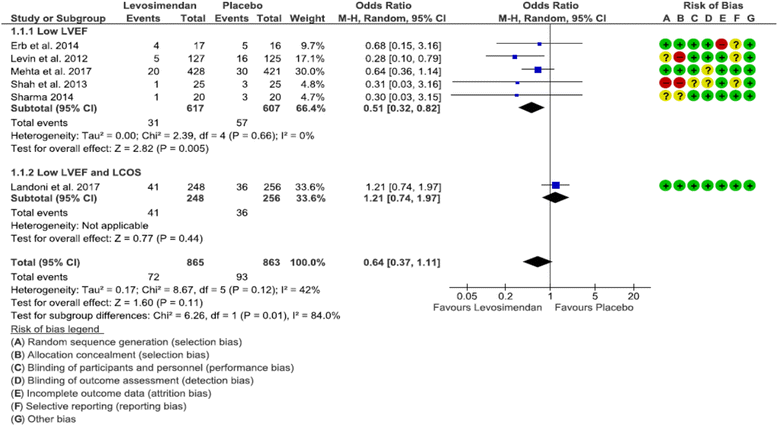
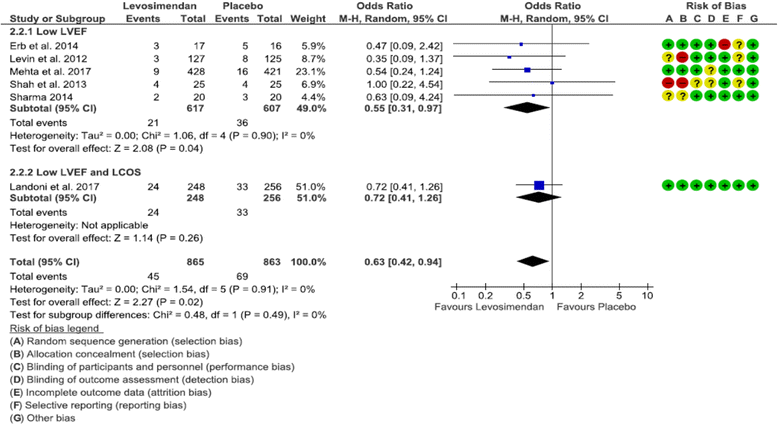
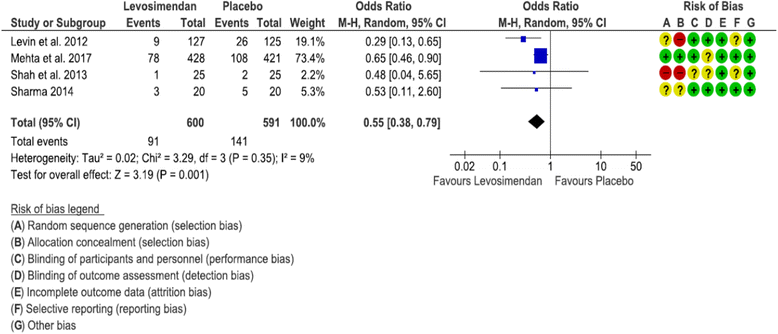
Results: Six RCTs were included in the meta-analysis, five of which investigated only patients with LVEF ≤ 35% and one of which included predominantly patients with LCOS. Mortality was similar overall (OR 0.64 [0.37, 1.11], p = 0.11) but lower in the subgroup with LVEF < 35% (OR 0.51 [0.32, 0.82], p = 0.005). Need for RRT was reduced by levosimendan both overall (OR 0.63 [0.42, 0.94], p = 0.02) and in patients with LVEF < 35% (OR 0.55 [0.31, 0.97], p = 0.04). Among secondary outcomes, we found lower postoperative LCOS in patients with LVEF < 35% receiving levosimendan (OR 0.49 [0.27, 0.89], p = 0.02), lower overall AKI (OR 0.62 [0.42, 0.92], p = 0.02), and a trend toward lower mechanical support, both overall (p = 0.07) and in patients with LVEF < 35% (p = 0.05).
Conclusions: Levosimendan reduces mortality in patients with preoperative severely reduced LVEF but does not affect overall mortality. Levosimendan reduces the need for RRT after high-risk cardiac surgery.
Keywords: Ejection fraction; Intensive care; Mortality; Renal replacement therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, et al. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(4):447–54. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000366. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bridgewater B, Grayson AD, Brooks N, Grotte G, Fabri BM, Au J, Hooper T, Jones M, Keogh B. Has the publication of cardiac surgery outcome data been associated with changes in practice in northwest England: an analysis of 25,730 patients undergoing CABG surgery under 30 surgeons over eight years. Heart. 2007;93(6):744–8. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2006.106393. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

