Protostemonine effectively attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice
- PMID: 29047459
- PMCID: PMC5758663
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2017.131
Protostemonine effectively attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice
Abstract
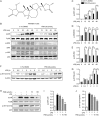
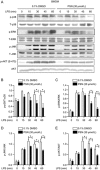
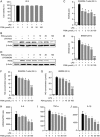
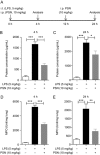
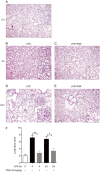
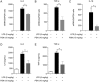
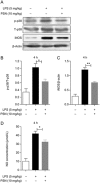
Protostemonine (PSN) is the main anti-inflammatory alkaloid extracted from the roots of Stemona sessilifolia (known as "Baibu" in traditional Chinese medicine). Here, we reported the inhibitory effects of PSN on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage activation in vitro and LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Macrophage cell line RAW264.7 cells and mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were treated with PSN (1, 3, 10, 30 and 100 μmol/L) for 0.5 h and then challenged with LPS (0.1 μg/mL) for 24 h. Pretreatment with PSN significantly inhibited LPS-induced phosphorylation of MAPKs and AKT, iNOS expression and NO production in the macrophages. C57BL/6 mice were intratracheally injected with LPS (5 mg/kg) to induce acute lung injury (ALI). The mice were subsequently treated with PSN (10 mg/kg, ip) at 4 and 24 h after LPS challenge. PSN administration significantly attenuated LPS-induced inflammatory cell infiltration, reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine (TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6) production and eliminated LPS-mediated lung edema. Furthermore, PSN administration significantly inhibited LPS-induced pulmonary MPO activity. Meanwhile, LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, iNOS expression and NO production in the lungs were also suppressed. The results demonstrate that PSN effectively attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo; the beneficial effects are associated with the decreased phosphorylation of MAPK and AKT and the reduced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as iNOS, NO and cytokines. These data suggest that PSN may be a potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of ALI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of novel curcumin analogs in experimental acute lung injury.Respir Res. 2015 Mar 24;16(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0199-1. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 25889862 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocostus Lactone Suppresses LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury and Macrophage Activation through NF-κB Signaling Pathway Mediated by p38 MAPK and Akt.Molecules. 2019 Apr 17;24(8):1510. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081510. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30999647 Free PMC article.
-
Cnidilide, an alkylphthalide isolated from the roots of Cnidium officinale, suppresses LPS-induced NO, PGE2, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α production by AP-1 and NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.021. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27591413
-
Protostemonine alleviates heat-killed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced acute lung injury through MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105964. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105964. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31669889
-
Picrasma quassiodes (D. Don) Benn. attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Sep;38(3):834-44. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2669. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27431288
Cited by
-
Ruscogenin attenuates particulate matter-induced acute lung injury in mice via protecting pulmonary endothelial barrier and inhibiting TLR4 signaling pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 May;42(5):726-734. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00502-6. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 32855531 Free PMC article.
-
Can natural products modulate cytokine storm in SARS-CoV2 patients?Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2022 Sep;35:e00749. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2022.e00749. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35702395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could natural products modulate early inflammatory responses, preventing acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19-confirmed patients?Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Feb;134:111143. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111143. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33360048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-deoxy-rutaecarpine protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-related inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 28;16:1522146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1522146. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39981175 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4 knockdown prevents inflammatory cytokine expression in macrophages by suppressing activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.Cell Biosci. 2019 Jul 3;9:55. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0315-x. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31304005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molloy RG, Mannick JA, Rodrick ML. Cytokines, sepsis and immunomodulation. Br J Surg 1993; 80: 289–97. - PubMed
-
- Medina EA, Morris IR, Berton MT. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation attenuates the TLR2-mediated macrophage proinflammatory cytokine response to francisella tularensis live vaccine strain. J Immunol 2010; 185: 7562–72. - PubMed
-
- Goodman RB, Pugin J, Lee JS, Matthay MA. Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2003; 14: 523–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

