Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation
- PMID: 29048367
- PMCID: PMC5666869
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18102188
Regulation of E2F1 Transcription Factor by Ubiquitin Conjugation
Abstract
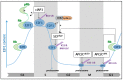
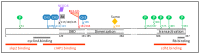
Ubiquitination is a post-translational modification that defines the cellular fate of intracellular proteins. It can modify their stability, their activity, their subcellular location, and even their interacting pattern. This modification is a reversible event whose implementation is easy and fast. It contributes to the rapid adaptation of the cells to physiological intracellular variations and to intracellular or environmental stresses. E2F1 (E2 promoter binding factor 1) transcription factor is a potent cell cycle regulator. It displays contradictory functions able to regulate both cell proliferation and cell death. Its expression and activity are tightly regulated over the course of the cell cycle progression and in response to genotoxic stress. I discuss here the most recent evidence demonstrating the role of ubiquitination in E2F1's regulation.
Keywords: DNA damage; E2F1; cell cycle; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

