Twitter-Based Detection of Illegal Online Sale of Prescription Opioid
- PMID: 29048960
- PMCID: PMC5678375
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2017.303994
Twitter-Based Detection of Illegal Online Sale of Prescription Opioid
Abstract
Objectives: To deploy a methodology accurately identifying tweets marketing the illegal online sale of controlled substances.
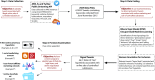
Methods: We first collected tweets from the Twitter public application program interface stream filtered for prescription opioid keywords. We then used unsupervised machine learning (specifically, topic modeling) to identify topics associated with illegal online marketing and sales. Finally, we conducted Web forensic analyses to characterize different types of online vendors. We analyzed 619 937 tweets containing the keywords codeine, Percocet, fentanyl, Vicodin, Oxycontin, oxycodone, and hydrocodone over a 5-month period from June to November 2015.
Results: A total of 1778 tweets (< 1%) were identified as marketing the sale of controlled substances online; 90% had imbedded hyperlinks, but only 46 were "live" at the time of the evaluation. Seven distinct URLs linked to Web sites marketing or illegally selling controlled substances online.
Conclusions: Our methodology can identify illegal online sale of prescription opioids from large volumes of tweets. Our results indicate that controlled substances are trafficked online via different strategies and vendors. Public Health Implications. Our methodology can be used to identify illegal online sellers in criminal violation of the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act.
Figures
Comment in
-
Buying Drugs Online in the Age of Social Media.Am J Public Health. 2017 Dec;107(12):1858-1859. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2017.304137. Am J Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29116843 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Understanding the epidemic. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/epidemic/index.html. Accessed August 6, 2017.
-
- Volkow ND, McLellan AT. Opioid abuse in chronic pain—misconceptions and mitigation strategies. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(13):1253–1263. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

