Clinical outcome and prognostic factors associated with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: An 11-year follow-up report from Taiwan
- PMID: 29049319
- PMCID: PMC5648178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186422
Clinical outcome and prognostic factors associated with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: An 11-year follow-up report from Taiwan
Abstract
Background: Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) has high mortality rate but prognostic factors are not well established. The aim of our study was to evaluate the trend in in-hospital mortality over a period of 11 years and identify factors affecting the clinical outcomes of patients with IPA.
Method: We conducted a nationwide inpatient population study using data from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database. A total of 407 IPA patients from 2002 to 2012 were included in the study. Differences in demographics, comorbidities, and treatment were evaluated between in-hospital death group and survival group. Multivariate analysis was also performed to identify risk factors for mortality.
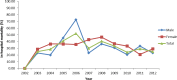
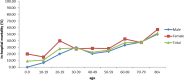
Result: Male patients represented 63.14% of the patients (n = 257) and the mean age was 53.15 ± 20.93 years. Hematological cancer (n = 216, 53.07%) and diabetes mellitus (n = 75, 18.43%) were the most common underlying conditions. The overall case fatality rate was 30.22% with female slightly higher then male (32.67% versus 28.79%). The in-hospital case fatality rate increased since 2002 and peaked in 2006. It then declined over time with an in-hospital mortality of 25% in 2012. The in-hospital death group had a higher intubation rate (p<0.0001), a longer ICU stay (p = 0.0062), higher percentages of DM (p = 0.0412) and COPD (p = 0.0178), and a lower percentage of hematological cancer (p = 0.0079) as compared to survivor. The in-hospital death group was more likely to have steroid treatment (p<0.0001), develop acute renal failure (p<0.0001) and other infectious diseases (p = 0.0008) during hospitalization. Multivariate analysis identified female gender, older age (≥ 65 years old), intubation, bone marrow transplantation, acute renal failure, other infectious diseases and steroid use as predictive factors for mortality.
Conclusion: The present study shows the trend in mortality among patients with IPA over an 11-year period. Female gender, older age, intubation, bone marrow transplantation, acute renal failure, other infectious diseases and steroid use were identified as risk factors for mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Galactomannan Testing and the Incidence of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A 10-Year Nationwide Population-Based Study in Taiwan.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 22;11(2):e0149964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149964. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26900697 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and outcome of invasive fungal infections in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients in a medical center in Taiwan.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018 Apr;51(2):251-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2016.08.011. Epub 2016 Dec 19. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018. PMID: 28089099
-
Risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and hospital mortality in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients: a retrospective-cohort study.Int J Med Sci. 2013 Sep 18;10(12):1625-31. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6824. eCollection 2013. Int J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24151434 Free PMC article.
-
[SENTIERI - Epidemiological Study of Residents in National Priority Contaminated Sites. Sixth Report].Epidemiol Prev. 2023 Jan-Apr;47(1-2 Suppl 1):1-286. doi: 10.19191/EP23.1-2-S1.003. Epidemiol Prev. 2023. PMID: 36825373 Italian.
-
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with influenza infection: A retrospective study and review of the literature.Clin Respir J. 2019 Apr;13(4):202-211. doi: 10.1111/crj.12995. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Clin Respir J. 2019. PMID: 30661296 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in an infant with chronic granulomatous disease.Respir Med Case Rep. 2022 Dec 12;41:101792. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2022.101792. eCollection 2023. Respir Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36568318 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Susceptibilities of Worldwide Isolates of Intrapulmonary Aspergillus Species and Important Candida Species in Sterile Body Sites against Important Antifungals: Data from the Antimicrobial Testing Leadership and Surveillance Program, 2017-2020.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0296522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02965-22. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36314941 Free PMC article.
-
Free circulating mircoRNAs support the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies and neutropenia.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 5;10(1):16532. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73556-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33020578 Free PMC article.
-
Surrogate infection model predicts optimal alveolar macrophage number for clearance of Aspergillus fumigatus infections.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2023 Apr 10;9(1):12. doi: 10.1038/s41540-023-00272-x. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2023. PMID: 37037824 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with hematological malignancies.Intensive Care Med. 2019 Dec;45(12):1732-1741. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05789-6. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Intensive Care Med. 2019. PMID: 31599334
References
-
- Taccone FS, Van den Abeele AM, Bulpa P, Misset B, Meersseman W, Cardoso T, et al. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: clinical presentation, underlying conditions, and outcomes. Critical care (London, England). 2015;19:7 Epub 2015/05/01. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0722-7 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4344741. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Montagna MT, Lovero G, Coretti C, Martinelli D, Delia M, De Giglio O, et al. SIMIFF study: Italian fungal registry of mold infections in hematological and non-hematological patients. Infection. 2014;42(1):141–51. Epub 2013/10/24. doi: 10.1007/s15010-013-0539-3 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3906525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun KS, Tsai CF, Chen SC, Chen YY, Huang WC. Correction: Galactomannan Testing and the Incidence of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A 10-Year Nationwide Population-Based Study in Taiwan. PloS one. 2016;11(6):e0156566 Epub 2016/06/02. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156566 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4889043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassetti M, Righi E, De Pascale G, De Gaudio R, Giarratano A, Mazzei T, et al. How to manage aspergillosis in non-neutropenic intensive care unit patients. Critical care (London, England). 2014;18(4):458 Epub 2014/08/30. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0458-4 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4220091. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nivoix Y, Velten M, Letscher-Bru V, Moghaddam A, Natarajan-Amé S, Fohrer C. Factors associated with overall and attributable mortality in invasive aspergillosis. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2008;47 doi: 10.1086/592255 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources