TMEM17 depresses invasion and metastasis in lung cancer cells via ERK signaling pathway
- PMID: 29050311
- PMCID: PMC5642586
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19977
TMEM17 depresses invasion and metastasis in lung cancer cells via ERK signaling pathway
Abstract
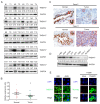
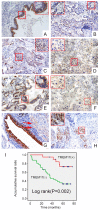
Transmembrane protein 17(TMEM17) is a newly identified protein, its expression pattern and clinicopathological relevance is still unclear. In this study, western blot assay was performed in 20 paired lung cancer samples and found that TMEM17 protein levels were lower in lung cancer tissues than that in the corresponding normal lung tissues (p=0.010). Immunohistochemistry staining in 143 cases lung cancer specimens also showed that TMEM17 expression in lung cancer tissues were significantly lower than adjacent normal lung tissues (35.7% vs 63.2%, p<0.001). And negative TMEM17 expression was significantly associated with poor histological differentiation (p=0.027), advanced TNM stages (p=0.006), positive lymph node metastasis (p=0.002) and poor prognosis (p=0.002). After overexpressing TMEM17, levels of p-ERK and its downstream molecules, p-P90RSK and Snail, were down-regulated, while levels of Occludin and Zo-1 were up-regulated, which result in the inhibition of invasion and migration ability of lung cancer cells. The effects were reversed by the incorporation of specific ERK inhibitor PD98059. In conclusion, loss of TMEM17 correlates with the development of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and predicts adverse clinical outcome of NSCLC patients. The effect of TMEM17 on inhibiting invasion and migration may attribute to restoring Occludin and Zo-1 expression through inactivating ERK-P90RSK-Snail pathway.
Keywords: ERK signaling; TMEM17; lung cancer; occludin and Zo-1; snail.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TMEM17 promotes malignant progression of breast cancer via AKT/GSK3β signaling.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Aug 2;10:2419-2428. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S168723. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30122991 Free PMC article.
-
Alex3 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer invasion via AKT/Slug/E-cadherin pathway.Tumour Biol. 2017 Jul;39(7):1010428317701441. doi: 10.1177/1010428317701441. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28705116
-
Lasp2 enhances tumor invasion via facilitating phosphorylation of FAK and predicts poor overall survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Dec;56(12):2558-2565. doi: 10.1002/mc.22700. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28667800
-
C14orf159 suppresses gastric cancer cells' invasion and proliferation by inactivating ERK signaling.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Feb 19;11:1717-1723. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S176771. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 30863180 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic TMEM88 promotes invasion and metastasis in lung cancer cells by binding DVLS.Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 1;75(21):4527-37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3828. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26359454
Cited by
-
Protein-protein interaction analysis reveals a novel cancer stem cell related target TMEM17 in colorectal cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 6;21(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01794-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33549114 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium induces A549 cell migration and invasion by activating ERK.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Sep;18(3):1793-1799. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7750. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31410139 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory role of puerarin on the A549 lung cancer cell line.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Nov;11(11):4117-4125. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-2246. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36523310 Free PMC article.
-
CAV2 promotes the growth of renal cell carcinoma through the EGFR/PI3K/Akt pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Sep 25;11:6209-6216. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S172803. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30288056 Free PMC article.
-
12 new susceptibility loci for prostate cancer identified by genome-wide association study in Japanese population.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 27;10(1):4422. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12267-6. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31562322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Soon YY, Stockler MR, Askie LM, Boyer MJ. Duration of chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3277–3283. - PubMed
-
- Williams MD, Sandler AB. The epidemiology of lung cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2001;105:31–52. - PubMed
-
- Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563–572. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD. Pathology of lung cancer. Clin Chest Med. 2011;32:669–692. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

