Immunomodulatory and antitumor effects of type I interferons and their application in cancer therapy
- PMID: 29050360
- PMCID: PMC5642635
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19531
Immunomodulatory and antitumor effects of type I interferons and their application in cancer therapy
Abstract
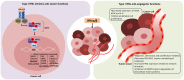
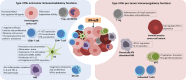
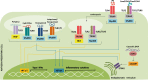
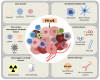
During the last decades, the pleiotropic antitumor functions exerted by type I interferons (IFNs) have become universally acknowledged, especially their role in mediating interactions between the tumor and the immune system. Indeed, type I IFNs are now appreciated as a critical component of dendritic cell (DC) driven T cell responses to cancer. Here we focus on IFN-α and IFN-β, and their antitumor effects, impact on immune responses and their use as therapeutic agents. IFN-α/β share many properties, including activation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and induction of a variety of cellular phenotypes. For example, type I IFNs drive not only the high maturation status of DCs, but also have a direct impact in cytotoxic T lymphocytes, NK cell activation, induction of tumor cell death and inhibition of angiogenesis. A variety of stimuli, including some standard cancer treatments, promote the expression of endogenous IFN-α/β, which then participates as a fundamental component of immunogenic cell death. Systemic treatment with recombinant protein has been used for the treatment of melanoma. The induction of endogenous IFN-α/β has been tested, including stimulation through pattern recognition receptors. Gene therapies involving IFN-α/β have also been described. Thus, harnessing type I IFNs as an effective tool for cancer therapy continues to be studied.
Keywords: IFNAR1/2; JAK-STAT; apoptosis; immunogenic cell death; necroptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that there is no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction and regulation of IFNs during viral infections.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004 Aug;24(8):439-54. doi: 10.1089/1079990041689665. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004. PMID: 15320958 Review.
-
Type I interferons and dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019;348:217-262. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31810554 Review.
-
Interferon: cellular executioner or white knight?Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(12):1279-89. doi: 10.2174/092986707780597907. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17504213 Review.
-
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and its role in interferon signaling.Pharmacol Ther. 2003 May;98(2):129-42. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(03)00016-0. Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12725866 Review.
-
Signaling Pathways of Type I and Type III Interferons and Targeted Therapies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Cells. 2019 Aug 23;8(9):963. doi: 10.3390/cells8090963. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31450787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perspectives for cancer immunotherapy mediated by p19Arf plus interferon-beta gene transfer.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018 Sep 6;73(suppl 1):e479s. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2018/e479s. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018. PMID: 30208166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic Cells and Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death: A Combination for Improving Antitumor Immunity.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Mar 12;12(3):256. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12030256. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32178288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Mechanisms and Future Opportunities for the Management of Radiation Necrosis in Patients Treated for Brain Metastases in the Era of Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 24;15(9):2432. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092432. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copy number alteration of the interferon gene cluster in cancer: Individual patient data meta-analysis prospects to personalized immunotherapy.Neoplasia. 2021 Sep 20;23(10):1059-1068. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2021.08.004. Online ahead of print. Neoplasia. 2021. PMID: 34555656 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid MyD88 restricts CD8+ T cell response to radiation therapy in pancreatic cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 May 27;13(1):8634. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35834-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37244938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Isaacs A, Lindenmann J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957;147:258–67. - PubMed
-
- Sin WX, Li P, Yeong JP, Chin KC. Activation and regulation of interferon-β in immune responses. Immunol Res. 2012;53:25–40. - PubMed
-
- Platanias LC. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:375–86. - PubMed
-
- Pestka S, Krause CD, Walter MR. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:8–32. - PubMed
-
- Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Smyth MJ, Kroemer G. Type I interferons in anticancer immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:405–14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

