Heart dosimetric analysis of three types of cardiac toxicity in patients treated on dose-escalation trials for Stage III non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29050957
- PMCID: PMC5705468
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.10.001
Heart dosimetric analysis of three types of cardiac toxicity in patients treated on dose-escalation trials for Stage III non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background and purpose: To assess associations between radiation dose/volume parameters for cardiac subvolumes and different types of cardiac events in patients treated on radiation dose-escalation trials.
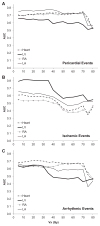
Material and methods: Patients with Stage III non-small-cell lung cancer received dose-escalated radiation (median 74 Gy) using 3D-conformal radiotherapy on six prospective trials from 1996 to 2009. Volumes analyzed included whole heart, left ventricle (LV), right atrium (RA), and left atrium (LA). Cardiac events were divided into three categories: pericardial (symptomatic effusion and pericarditis), ischemia (myocardial infarction and unstable angina), and arrhythmia. Univariable competing risks analysis was used.
Results: 112 patients were analyzed, with median follow-up 8.8 years for surviving patients. Nine patients had pericardial, seven patients had ischemic, and 12 patients had arrhythmic events. Pericardial events were correlated with whole heart, RA, and LA dose (eg, heart-V30 [p=0.024], RA-V30 [p=0.013], and LA-V30 [p=0.001]), but not LV dose. Ischemic events were correlated with LV and whole heart dose (eg, LV-V30 [p=0.012], heart-V30 [p=0.048]). Arrhythmic events showed borderline significant associations with RA, LA, and whole heart dose (eg, RA-V30 [p=0.082], LA-V30 [p=0.076], heart-V30 [p=0.051]). Cardiac events were associated with decreased survival on univariable analysis (p=0.008, HR 2.09), but only disease progression predicted for decreased survival on multivariable analysis.
Conclusions: Cardiac events were heterogeneous and associated with distinct heart subvolume doses. These data support the hypothesis of distinct etiologies for different types of radiation-associated cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: Cardiac toxicity; Chemoradiation; Dose escalation; NSCLC.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Dautzenberg B, Arriagada R, Chammard AB, et al. A controlled study of postoperative radiotherapy for patients with completely resected nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Groupe d’Etude et de Traitement des Cancers Bronchiques. Cancer. 1999;86(2):265–273. - PubMed
-
- Lally BE, Detterbeck FC, Geiger AM, et al. The risk of death from heart disease in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer who receive postoperative radiotherapy: analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. Cancer. 2007;110(4):911–917. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Rosell R, De Lena M, et al. Impact of postoperative radiation therapy on survival in patients with complete resection and stage I, II, or IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer treated with adjuvant chemotherapy: the adjuvant Navelbine International Trialist Association (ANITA) Randomized Trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;72(3):695–701. - PubMed
-
- Bradley JD, Paulus R, Komaki R, et al. Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): a randomised, two-by-two factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(2):187–199. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

