HMGA1 is a novel transcriptional regulator of the FoxO1 gene
- PMID: 29052178
- PMCID: PMC5845622
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-017-1445-8
HMGA1 is a novel transcriptional regulator of the FoxO1 gene
Abstract
Purpose: The forkhead transcription factor (FoxO1) is a master transcriptional regulator of fundamental cellular processes ranging from cell proliferation and differentiation to inflammation and metabolism. However, despite its relevance, the mechanism(s) underlying FoxO1 gene regulation are largely unknown. We have previously shown that the chromatin factor high-mobility group A1 (HMGA1) plays a key role in the transcriptional regulation of glucose-responsive genes, including some that are involved in FoxO1-mediated glucose metabolism. Here we investigated the impact of HMGA1 on FoxO1 gene expression.
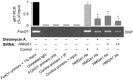
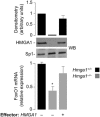
Methods: FoxO1 protein and gene expression studies were performed by Western blot analysis combined with qRT-PCR of material from human cultured cells and EBV-transformed lymphoblasts, and from primary cultured hepatocytes from wild-type and Hmga1 -/- mice. Reporter gene assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation for binding of HMGA1 to the endogenous FoxoO1 locus were performed in cells overexpressing HMGA1 and in cells pretreated with siRNA targeting HMGA1.
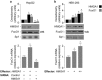
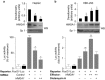
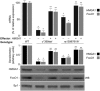
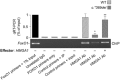
Results: HMGA1 increased FoxO1 mRNA and protein expression in vitro, in cultured HepG2 and HEK-293 cells by binding FoxO1 gene promoter, thereby activating FoxO1 gene transcription. Forced expression of HMGA1 in primary cultured hepatocytes from Hmga1 -/- mice and in EBV-transformed lymphoblasts from subjects with reduced expression of endogenous HMGA1 increased FoxO1 mRNA and protein levels.
Conclusion: These findings may contribute to the understanding of FoxO1 gene regulation and its role in metabolism.
Keywords: DNA/chromatin interaction; FoxO1; Gene transcription; HMGA1; Insulin signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross-talk among HMGA1 and FoxO1 in control of nuclear insulin signaling.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 4;8(1):8540. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26968-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29867121 Free PMC article.
-
HMGA1 down-regulation is crucial for chromatin composition and a gene expression profile permitting myogenic differentiation.BMC Cell Biol. 2010 Aug 11;11:64. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-64. BMC Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20701767 Free PMC article.
-
HMGA1 protein is a positive regulator of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene.Eur J Cancer. 2010 Jul;46(10):1919-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.050. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Eur J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20335021
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Glucose Metabolism: The Emerging Role of the HMGA1 Chromatin Factor.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jul 3;9:357. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00357. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30034366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1) Transcriptome in Cancer and Development.Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(4):353-93. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160316152147. Curr Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26980699 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Major Outer Membrane Protein from Legionella pneumophila Inhibits Phagocytosis but Enhances Chemotaxis of RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Regulating the FOXO1/Coronin-1 Axis.J Immunol Res. 2021 Nov 13;2021:9409777. doi: 10.1155/2021/9409777. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34812410 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Important Transcription Factors and Biological Processes in Skin Regeneration Mediated by Mechanical Stretch.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 29;12:757350. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.757350. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34659370 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk among HMGA1 and FoxO1 in control of nuclear insulin signaling.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 4;8(1):8540. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26968-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29867121 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of FOXO1 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary endothelial injury by induction of autophagy.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jun;10(11):630. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5380. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35813334 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of energy metabolism in human pluripotent stem cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):8097-8108. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04016-0. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34773132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

