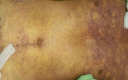
Purpura Fulminans: A rare presentation of Streptococcus Pneumoniae infection
- PMID: 29054893
- PMCID: PMC5665333
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221150
Purpura Fulminans: A rare presentation of Streptococcus Pneumoniae infection
Abstract
A previously healthy man presented with fever for 2 days and rapidly progressive purpuric rash for 1 day. He progressed into hypotension, disseminated intravascular coagulation and refractory shock despite resuscitation and early antibiotic commencement. Blood culture grew Streptococcus pneumoniae This case report highlights the fact that purpura fulminans can be a rare presentation of S. pneumoniae infection as well.
Keywords: adult intensive care; infectious diseases.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Pinky Jha, Sierra Jin BS. A case of acute purpura fulminans caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Consultant 2016;56:1010–2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical