ALK Inhibitor Response in Melanomas Expressing EML4-ALK Fusions and Alternate ALK Isoforms
- PMID: 29054983
- PMCID: PMC5752582
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0472
ALK Inhibitor Response in Melanomas Expressing EML4-ALK Fusions and Alternate ALK Isoforms
Abstract
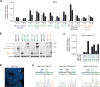
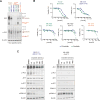
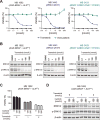
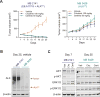
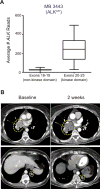
Oncogenic ALK fusions occur in several types of cancer and can be effectively treated with ALK inhibitors; however, ALK fusions and treatment response have not been characterized in malignant melanomas. Recently, a novel isoform of ALK (ALKATI ) was reported in 11% of melanomas but the response of melanomas expressing ALKATI to ALK inhibition has not been well characterized. We analyzed 45 melanoma patient-derived xenograft models for ALK mRNA and protein expression. ALK expression was identified in 11 of 45 (24.4%) melanomas. Ten melanomas express wild-type (wt) ALK and/or ALKATI and one mucosal melanoma expresses multiple novel EML4-ALK fusion variants. Melanoma cells expressing different ALK variants were tested for response to ALK inhibitors. Whereas the melanoma expressing EML4-ALK were sensitive to ALK inhibitors in vitro and in vivo, the melanomas expressing wt ALK or ALKATI were not sensitive to ALK inhibitors. In addition, a patient with mucosal melanoma expressing ALKATI was treated with an ALK/ROS1/TRK inhibitor (entrectinib) on a phase I trial but did not respond. Our results demonstrate ALK fusions occur in malignant melanomas and respond to targeted therapy, whereas melanomas expressing ALKATI do not respond to ALK inhibitors. Targeting ALK fusions is an effective therapeutic option for a subset of melanoma patients, but additional clinical studies are needed to determine the efficacy of targeted therapies in melanomas expressing wt ALK or ALKATIMol Cancer Ther; 17(1); 222-31. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–6. - PubMed
-
- Lin E, Li L, Guan Y, Soriano R, Rivers CS, Mohan S, et al. Exon array profiling detects EML4-ALK fusion in breast, colorectal, and non-small cell lung cancers. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:1466–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

